What Is Hyper-V Resilient Change Tracking: Using RCT for VM Backup
When it comes to backup efficiency and copying only unique data blocks between full backups (that is, creating incremental backups), change tracking technology is extremely important. VMware’s Changed Block Tracking (CBT) has been available for a long time and is familiar to many when it comes to creating backups in virtual environments. A similar feature is available for Microsoft Hyper-V environments. Microsoft calls its own technology Resilient Change Tracking (RCT). Let’s take a look at this technology in Windows Server 2016 and learn how it is implemented.
What Is Hyper-V RCT?
Resilient Change Tracking (RCT) is a feature of Microsoft Hyper-V that tracks disk blocks that have changed since the last backup of a virtual machine (VM). As a result, when running the next incremental backup of the VM, only changed blocks are copied to backup storage.
While this technology has been around in the VMware world since ESX/ESXi 4.0 and virtual machine version 7 and higher (since around 2011), in the Hyper-V world, this is a relatively new technology. IT wasn’t until the introduction of RCT in Windows Server 2016 that we got an efficient way to keep track of these changed blocks in Hyper-V VMs.
Before 2016, Hyper-V change tracking was accomplished by proprietary filter drivers implemented by backup vendors to copy only changed blocks from source Hyper-V VMs to a repository.
Note: Hyper-V VM configuration version must be 6.2 or higher to be able to use RCT.
Let’s now find out why Hyper-V Resilient Change Tracking is essential for backup solutions.
Why Use Hyper-V RCT
In the context of a virtualized environment, when you create a full VM backup, you get a complete representation of that VM block by block. It is recommended that the next backup should ideally be an incremental backup with only changed blocks copied from the source machine. It would be extremely inefficient to copy duplicate data over and over again if we already have that data in our backup repository. Creating full backups for every cycle means long backup windows transferring unnecessary data to the repository and high backup storage capacity requirements.
Here’s where change tracking technology comes in. By leveraging Microsoft’s RCT, third-party data protection solutions can create faster and more efficient incremental backups and replicas, copying only changed blocks of data after a full backup.
How Hyper-V RCT Works During Backups
Resilient Change Tracking in Hyper-V creates a mapping of all the blocks of data used by a virtual machine. On the next backup cycle, the changed tracking information knows which blocks have changed since the last backup. Only those changed blocks are copied in the subsequent backup cycles.
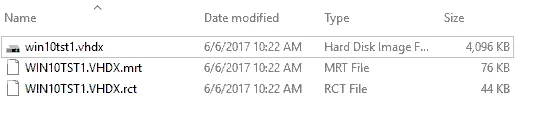
The resilient change tracking references Hyper-V’s ability to be able to keep track of changes even if we have a hard crash or unexpected power off of the virtual machine. Windows Server 2016 Hyper-V accomplishes this by implementing three change tracking files: 1 in memory and 2 on disk. This way, if the above-mentioned dirty shutdown or power off happens and the changed tracking in memory is lost, we still have the changed tracking on disk. There are two files that get created when the first full backup of a Windows Server 2016 Hyper-V is done.
During the checkpoint creation process during the backup, you will also see a .vhdx file created for the disk as well as the .mrt and .rct files. If you don’t see these files created during the VM backup operation, then you have not initiated an RCT backup operation. Most likely, you have selected a backup operation with a proprietary backup solution filter driver enabled.
After the checkpoint has been rolled off and the backup job is completed, we are left with the .vhdx, .mrt and .rct files.
Let’s explain what these files are used for.
- The RCT or Resilient Change Tracking file is the most detailed representation of changed blocks on disk (though less detailed than mapping in memory). This file is written in write-back or cached mode, which means that it is used during regular VM operations such as migrations, startups, shutdowns, etc.
- The MRT or Modified Region Table file is written in write-through mode and is less granular than the RCT file, though it records all the changes on disk. If something happens – a crash, power failure, etc. – the MRT file is used to reconstruct the changed blocks. This will save a great amount of time and be more efficient than a full backup of the VM.
Why we need change tracking files on disk
The memory mapping of changed blocks that is kept is only good for the VM as long as it lives on the same host. If that host crashes or the VM is migrated to a new host, the in-memory changed blocks mapping is lost. As shown above, Windows Server 2016 Resilient Change Tracking with the new RCT and MRT files resolves this issue as the changed block tracking is persisted to disk and can be referenced without dependencies on the computer and memory resources that own the VM.
Using Hyper-V RCT for VM Backup with NAKIVO Backup & Replication
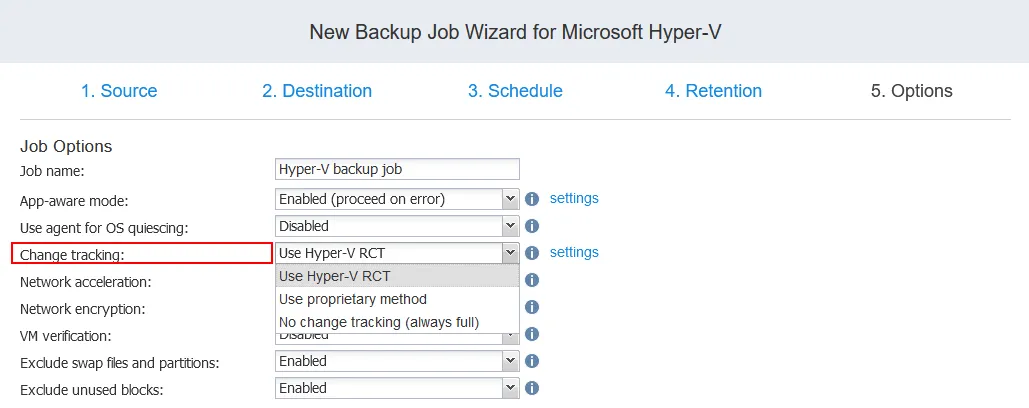
When you create a Microsoft Hyper-V backup job in the NAKIVO solution, you can configure Hyper-V RCT settings for one or multiple VMs added to the backup job. If you use Hyper-V 2016 or newer on a server from which you back up the VMs, you can use native Hyper-V RCT. Hyper-V VM backup options contain three change tracking options:
- Use Hyper-V RCT
- Use proprietary method
- No change tracking (always full)
Hyper-V RCT is the most effective option with the lowest load on a Hyper-V host with the source VMs to back up. The Hyper-V RCT option is not available for VMs running on Hyper-V 2012.
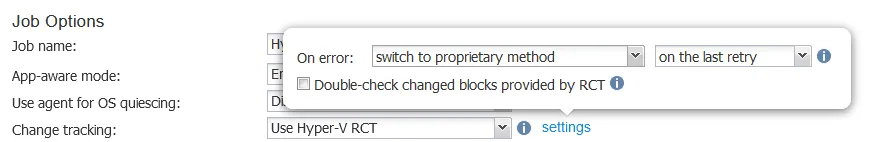
You can edit settings and set behavior in case the solution encounters errors while using RCT:
- Switch to proprietary method
- Fail VM processing
Also, in the settings configuration for change tracking, you can select to double-check the changed blocks provided by RCT. As the tooltip notes (when you click ⓘ), this results in longer job runs for additional verification of change tracking between backup cycles.
Conclusion
Resilient Change Tracking is a useful Hyper-V feature for incremental VM backup. This change tracking feature is available in Hyper-V 2016, 2019, and newer versions. Now changed blocks are effectively tracked at the hypervisor level. Data protection vendors like NAKIVO use RCT via special APIs instead of writing their own change tracking filters for more efficient backup and replication.