How to Restart Management Agents on a VMware ESXi Host
VMware ESXi is a hypervisor that is part of the VMware vSphere virtualization platform. All virtualization software can have issues at some point. In vSphere, for example, you may not be able to connect to an ESXi or connect an ESXi host to vCenter, or error messages are displayed in vCenter and you cannot create VMs. Restarting the ESXi host can help you in some cases. But you will have to shut down virtual machines (VMs) or migrate them to another host, which is a problem in a production environment. It is better to restart the ESXi management agents first. It is very likely that restarting management agents on an ESXi host can resolve the issue.
Symptoms
Let me start by listing the common symptoms for the need to restart ESXi management agents on a server:
- It is not possible to connect to an ESXi host directly or manage this host under vCenter.
- An ESXi host is disconnected from vCenter, but VMs continue to run on the ESXi host.
- vCenter displays the following error when you try to create a virtual machine (VM):
Virtual machine creation may fail because the agent is unable to retrieve VM creation options from the host
- VM migration between ESXi hosts is not performed and the following error is returned:
Relocate virtual machine
The operation is not allowed in the current connection state of the host
- Information about a running VM is not displayed in the Summary tab when you select a VM:
CPU Usage – 0 MHz
Memory Usage – 0.00 MB
The Role of ESXi Management Agents
ESXi management agents are used to synchronize VMware components and make it possible to access an ESXi host from vCenter Server. VMware agents are included in the default configuration and are installed when you are installing ESXi. There are two main agents on ESXi that may need to be restarted if connectivity issues occur on the ESXi host – hostd and vpxa.
hostd is a host agent responsible for managing most of the operations on an ESXi host and registering VMs, visible LUNs, and VMFS volumes. hostd is responsible for starting and stopping VMs and similar major tasks. VMware hostd is used for communication between ESXi and vmkernel.
vpxa is the VMware agent activated on an ESXi host when the ESXi host joins vCenter Server. There is also the instance in which vpxd on vCenter Server communicates with vpxa on ESXi hosts (vpxa is the VMware agent running on the ESXi side and vpxd is the daemon running on the vCenter side). vpxa communicates with hostd on ESXi hosts. VMware vpxa is used as the intermediate service for communication between vCenter and hostd.
If you use vSphere Client and vCenter to manage an ESXi host, vCenter passes commands to the ESXi host through the vpxa process running on the ESXi host. If you are connecting directly to an ESXi host to manage the host, then communication is established directly to the hostd process on the host for management.
How Are VMs Affected?
Virtual machines are not restarted or powered off when you restart ESXi management agents (you don’t need to restart virtual machines). If you want to ensure that VMs are not affected, try to ping one of the VMs running on the ESXi host and restart VMware agents on this ESXi host. Tasks running on the ESXi hosts can be affected or interrupted. Make sure that there are no VMware VM backup jobs running on the ESXi host at the moment that you are restarting the ESXi management agents.
The ESXi host and VMs on that host are displayed as disconnected for a moment while ESXi management agents are being restarted on the ESXi host. Refresh the page in VMware vSphere Client after a few seconds and the status of the ESXi host and VMs should be healthy.
To avoid issues, read the precautions at the end of the blog post before using ESXi to restart the VMware agents if you use vSAN, NSX, or shared graphics in your VMware virtual environment.
Restarting Agents in the Direct Console UI
The most reliable method to restart ESXi management agents is to use the ESXi Direct Console User Interface (DCUI). You must have physical access to the ESXi server with a keyboard and monitor connected to the server. Services used for ESXi network management might not be responsible and you may not be able to manage a host remotely, for example, via SSH.
- Press F2 to customize system settings in the DCUI.
- Enter a username and password for an administrative account (root is the default account with administrative permissions on ESXi).
Note: Please be patient. Sometimes you can encounter a significant lag. The delay between entering credentials and the server reaction to this action can take a few minutes. The timeout can be caused by waiting for a response from the hanging management services that must be restarted.
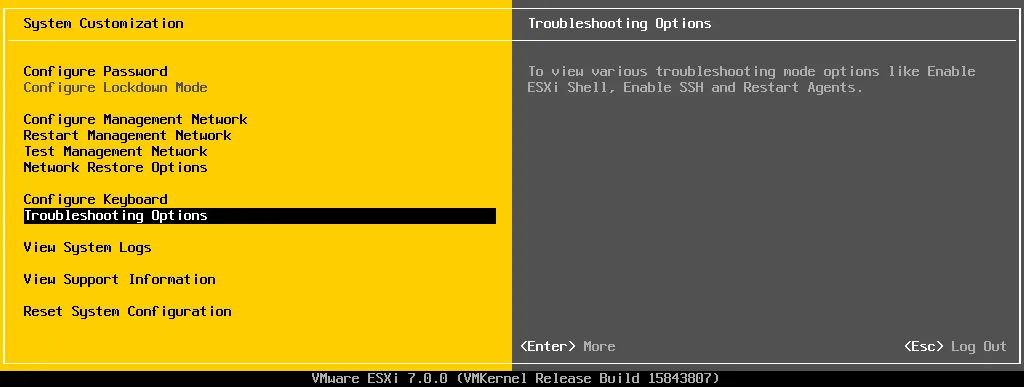
- After accepting credentials, you should see the System Customization menu.
- Select Troubleshooting Options and press Enter. In the right pane of the DCUI, you can see useful tips after selecting an option in the menu.
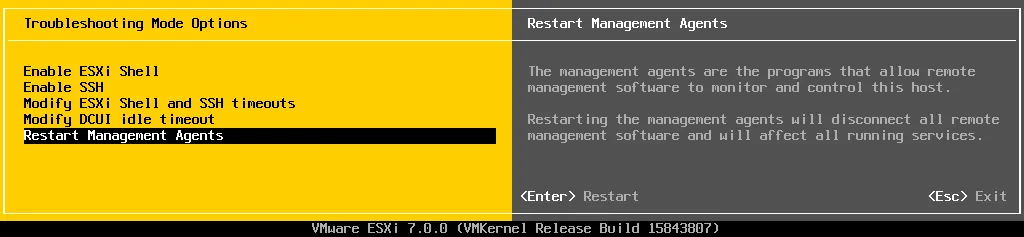
- Select Restart Management Agents in Troubleshooting Mode Options and press Enter.
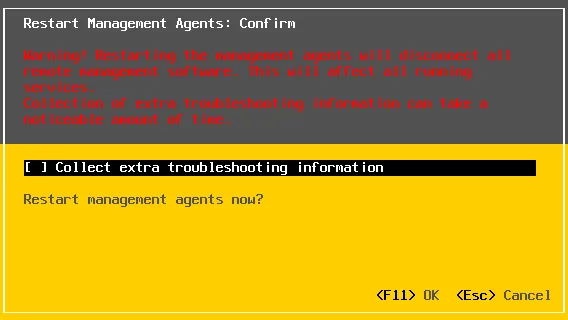
- The configuration message appears regarding restart management agents. You can press Space to collect extra troubleshooting information (optional). Hit F11 to confirm and restart management agents now.
- Wait until ESXi management agents restart and then check whether the issues are resolved.
- If restarting the management agents in the DCUI doesn’t help, you may need to view the system logs and run commands in the ESXi command line by accessing the ESXi shell directly or via SSH. You can enable the ESXi shell and SSH in the DCUI. SSH access and ESXi shell are disabled by default.
- In order to enable ESXi shell go to Troubleshooting Options, select Enable ESXi Shell, and press Enter.
- In order to enable remote SSH access, go to Troubleshooting Options, select Enable SSH, and press Enter.
Using VMware Host Client
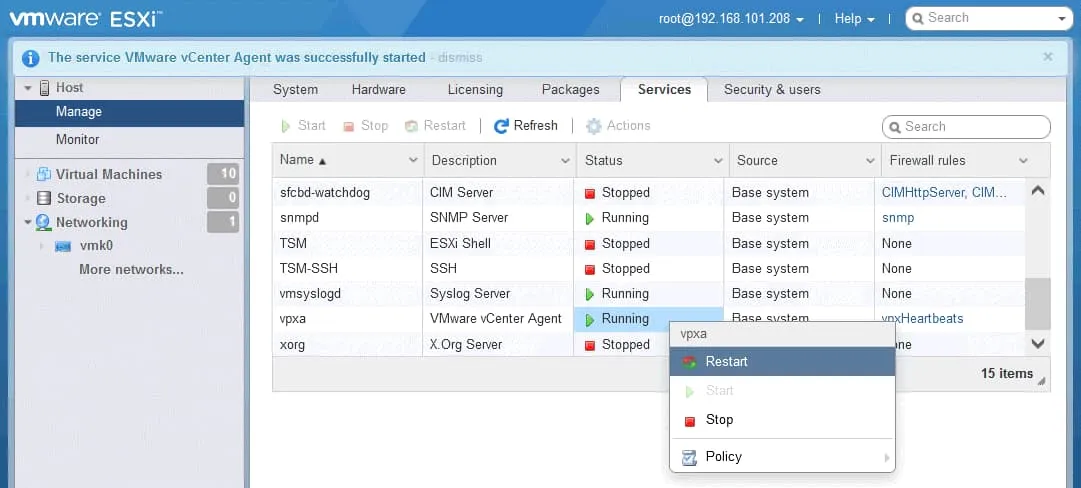
Using VMware Host Client is convenient for restarting VMware vCenter Agent, vpxa, which is used for connectivity between an ESXi host and vCenter.
- Enter the IP address of your ESXi host in the address bar of a web browser. Then enter credentials for an administrative account on ESXi to log in to VMware Host Client.
- In the Navigation pane, go to Host > Manage, and select the Services tab.
- Right-click the vpxa service and, in the context menu, press Restart.
If you cannot open VMware Host Client, use other methods to restart ESXi management agents. You can start the TSM-SSH service to enable remote SSH access to the ESXi host.
Restarting VMware Agents in ESXi Shell (SSH)
ESXi command-line interface (CLI) is a powerful tool for managing an ESXi host and for troubleshooting. SSH access to the ESXi host must be enabled for remote management. Use an SSH client for connecting to an ESXi host remotely and using the command-line interface. You can use PuTTY on a Windows machine as the SSH client. Define the IP address or a hostname of the ESXi server, select the port (22 by default), and then enter administrative credentials in the SSH client. You should then see the console (terminal) session via SSH.
If you want to use ESXi shell directly (without remote access), you must enable ESXi shell, and use a keyboard and monitor physically attached to the ESXi server. Read the blog post about ESXCLI to learn more about ESXi command-line options.
Note: Commands used in this blog post are compatible with ESXi 6.x and ESXi 7.x.
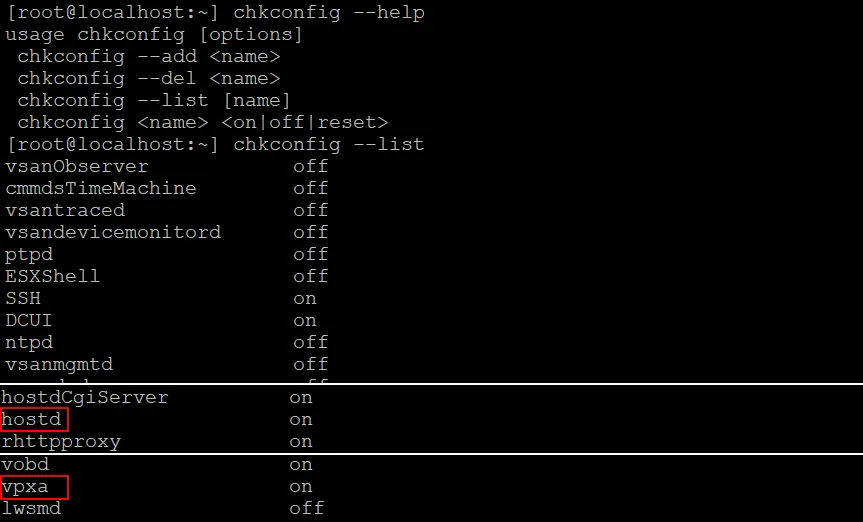
- List all services available on the ESXi host (optional) with the command:
chkconfig –list - Find the hostd and vpxa services in the console output and check their status.
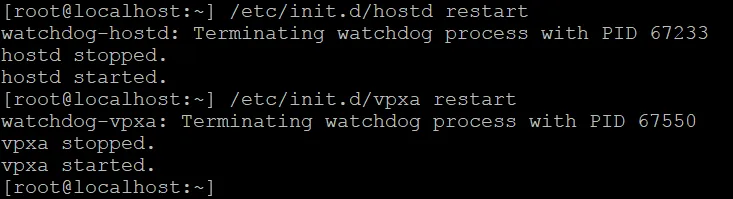
- Restart the hostd and vpxa services (management agents) with the commands:
/etc/init.d/hostd restart
/etc/init.d/vpxa restart
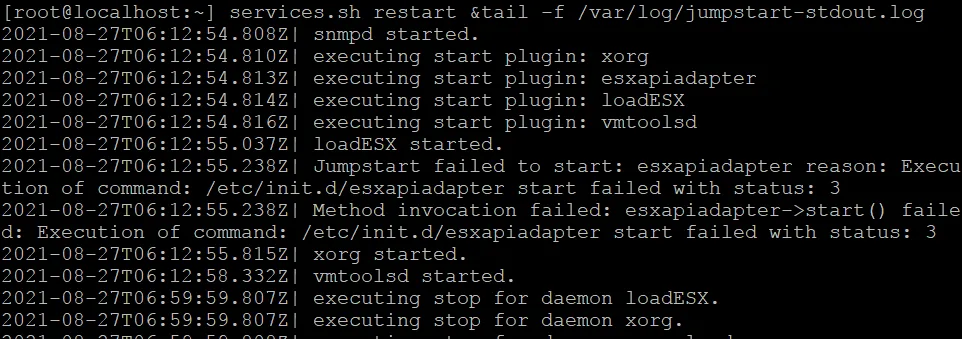
- Use this command as an alternative, to restart all management agents on the ESXi host.
services.sh restart &tail -f /var/log/jumpstart-stdout.log
The progress of the VMware agents restart is displayed in the console output.
- You can also try to reset the management network on a VMkernel interface:
esxcli network ip interface set -e false -i vmk0; esxcli network ip interface set -e true -i vmk0
The vmk0 interface is used by default on ESXi. If you have a different name for the management network interface, use the appropriate interface name in the command.
This complex command consists of two basic commands separated by ; (semicolon). The vmk0 management network interface is disabled by the first part of the command. When this part is executed successfully and vmk0 is down, then the second part of the command is executed to enable the vmk0 interface. As a result, the ESXi management network interface is restarted.
Using DCUI via SSH
If you have SSH access to an ESXi host, you can open the DCUI in the SSH session. This method allows you to use a pseudo-graphical user interface of the DCUI in the console for more convenience.
- Run the command to open the DCUI in the console/terminal:
dcui - Press F2 to customize the system.
- Select the needed options to restart VMware management agents as explained in the section above where the DCUI was explained.
Using PowerCLI to Restart VMware Management Agents
VMware PowerCLI is another tool based on Windows PowerShell to manage vCenter and ESXi hosts in the command line interface.
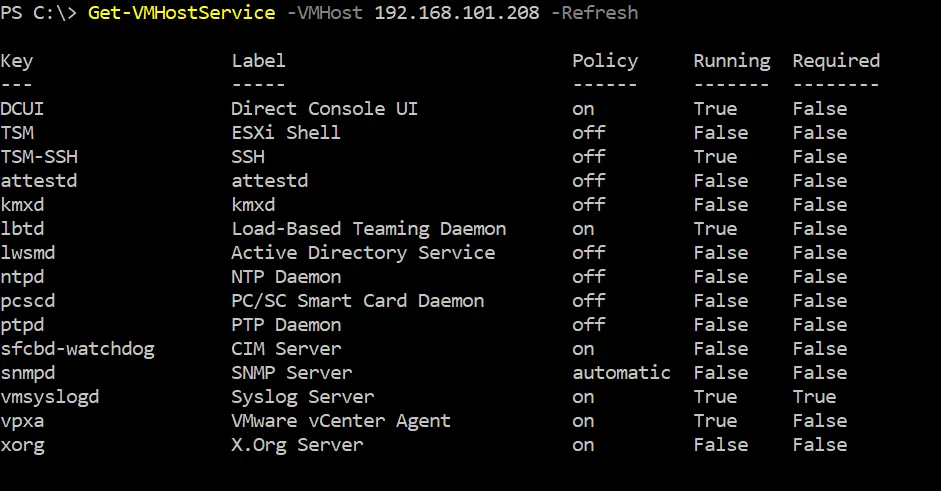
- Get the list of available services on the ESXi host:
Get-VMHostService -VMHost 192.168.101.208 -Refresh- The -Refresh parameter is used to refresh data before printing this data in the console.
- 192.168.101.208 is the IP address of the ESXi host used in this example.
- Define the name or IP address of your ESXi host according to your configuration. The list of services displayed in the output is similar to the list of services displayed in VMware Host Client rather than the list of services displayed in the ESXi command line.
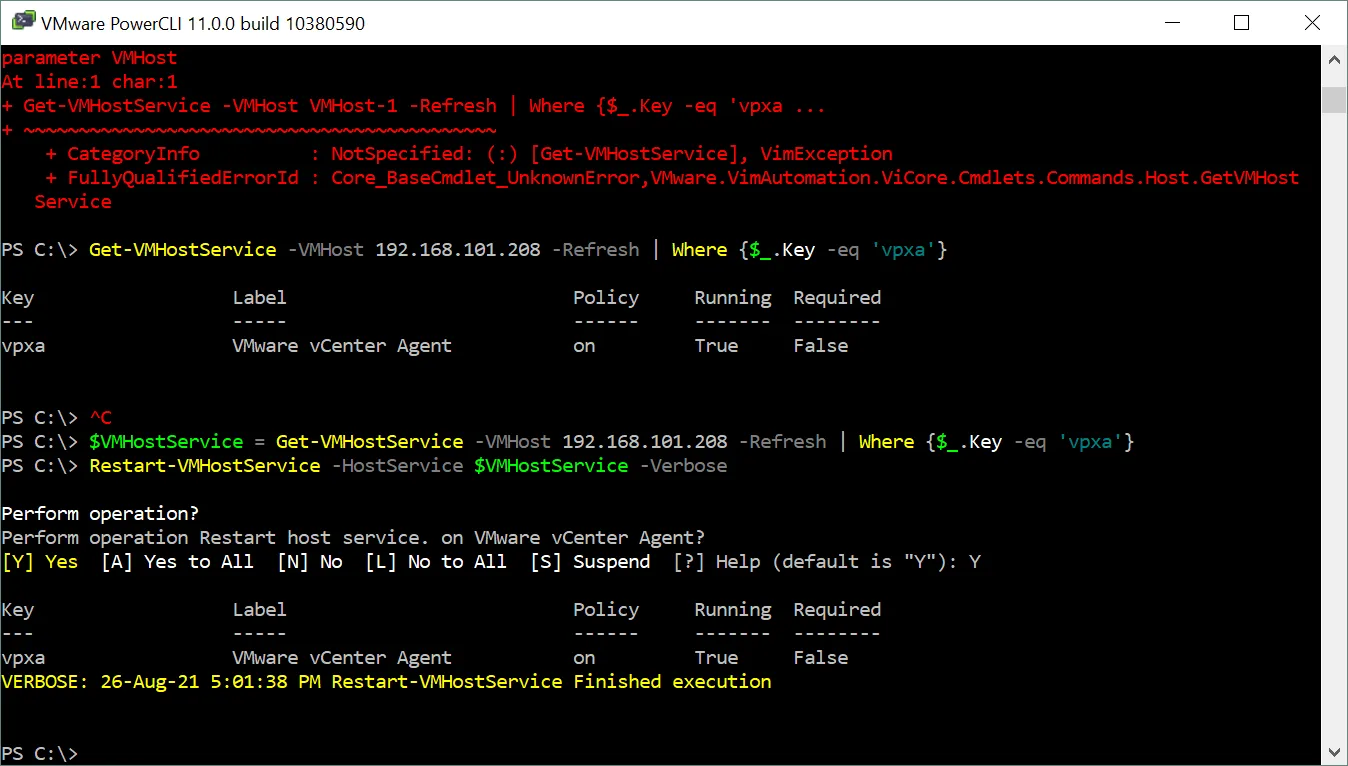
- Specify the host and service for adding the value to the $VMHostService variable
$VMHostService = Get-VMHostService -VMHost 192.168.101.208 -Refresh | Where {$_.Key -eq ‘vpxa’}
where vpxa is the name of the needed ESXi Management service. You can also define another service that you want to start, stop, or restart, for example, TSM-SSH (the SSH server service on an ESXi host). - Restart the vpxa service by using the $VMHostService variable in the command:
Restart-VMHostService -HostService $VMHostService -Verbose
- You can also manually stop and start a service:
Stop-VMHostService -HostService $VMHostService
Start-VMHostService -HostService $VMHostService
- You can try to use the alternative command to restart vpxa:
Get-VMHostService -VMHost 192.168.101.208 | where {$_.Key -eq “vpxa”} | Restart-VMHostService -Confirm:$false -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
Precautions
- If Link Aggregation Control Protocol (LACP) is used on an ESXi host that is a member of a vSAN cluster, don’t restart ESXi management agents with the services.sh command.
Use /etc/init.d/module restart to restart the independent services. - If NSX is configured in your VMware virtual environment, don’t use the /sbin/services.sh restart command. This command restarts all services on an ESXi host and network connections are temporarily interrupted. In this case, you should individually restart vpxa, hostd, and fdm to restart ESXi management agents on the host. If restarting agents individually doesn’t help and you need to run a /sbin/services.sh restart, then migrate VMs from the current ESXi host and put the host into the maintenance mode.
- If you don’t know whether NSX is installed on an ESXi host, you can use this command to find out:
/sbin/services.sh restartesxcli software vib list –rebooting-image | grep esx-* - If vsip-esx and esx-vxlan VIBs are displayed in the output, then NSX for vSphere is installed on the ESXi host.
- If shared graphics is used in a VMware View environment (VGPU, vSGA, vDGA), don’t use services.sh to restart ESXi agents. If you restart management agents with the services.sh command, then the xorg service that is responsible for graphics of the guest operating systems is stopped. Disabling graphics in guest operating systems causes the virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI) to crash where shared graphics are used. You can restart hostd and vpxa manually if you are using shared graphics and an ESXi host is not entered into maintenance mode.
Conclusion
Restarting ESXi management agents can help you resolve issues related to the disconnected status of an ESXi host in vCenter, errors that occur when connecting to an ESXi host directly, issues with VM actions, etc. This blog post has covered common methods to restart ESXi management agents by using the DCUI, ESXi command line, VMware Host Client, and VMware PowerCLI. In general, virtual machines are not affected by restarting agents, but more attention is needed if vSAN, NSX, or shared graphics for VDI are used in the vSphere virtual environment.
Back up your VMware VMs in vSphere regularly to protect data and have the ability to quickly recover data and restore workloads. NAKIVO Backup & Replication is the all-in-one data protection solution that supports the backup of VMs in VMware vSphere. The product can be installed on Windows, Linux, NAS devices, and as a VMware virtual appliance.