What is ReFS File System: Benefits and Best Practices
Windows Server 2019 offers many exciting benefits across the board. However, when thinking about storage features with this release and, more importantly, how they affect backups, one feature we want to take a closer look at is Windows Server 2019 ReFS file system version 3.4. It offers huge improvements over previous file systems in certain use cases as well as predecessor versions of ReFS found in Windows Server 2012 and 2016.
What Is the ReFS File System?
The ReFS file system, which stands for Resilient File System, is the newest file system developed by Microsoft, with the first version released with Windows Server 2012. It gets its name from the resiliency features in this file system. In addition to resiliency, the Microsoft file system is designed with the goals of maximizing availability, scalability, and integrity. You can create volumes with this file system in Windows Server 2019 and Windows 10 Pro for Workstations.
Administrators no longer have to worry about running the chkdsk utility, which detects errors in the file system. This is due in part to ReFS having the ability to perform online checks of the file system health in real-time.
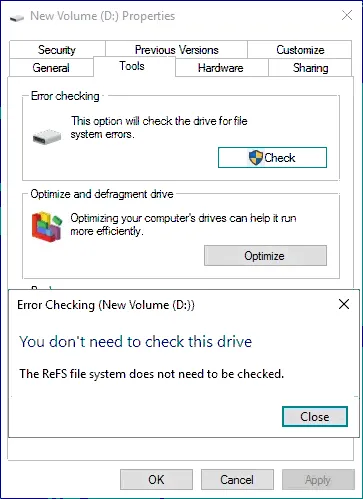
ReFS uses checksums that allow it to detect any data corruption and recover from that corruption quickly. In fact, if you look at a ReFS formatted volume and run Tools > Check on the volume, you receive the message: You don’t need to check this drive. The ReFS file system does not need to be checked.
Windows Server 2019 ReFS Benefits
Two of the use cases where ReFS really shines are in the areas of virtualization and use by modern backup solutions. Some of the high-level benefits of the Windows Server 2019 ReFS file system are:
- ReFS takes advantage of B+ trees in the file structure. B+ tree is very efficient in storing data as there is a very high fanout of children nodes in the structure. By using pointers, the B+ tree can reduce the amount of I/O operations to retrieve an element in the tree.
- The maximum volume size for ReFS is 1 yottabyte or 1 trillion terabytes!
- File metadata is periodically scrubbed by reading and performing checksum operations on the data. This new scrubber is another mechanism to ensure file resiliency.
- File integrity streams provide additional file data checksums.
Note: With the added resiliency benefits, ReFS is the recommended file system for Exchange Server 2019 database/log locations.
- Windows Server 2019 ReFS includes the block cloning technology. This allows for pointer references to blocks that would otherwise have to be moved around.
- Copy on write is a mechanism used by ReFS to ensure integrity when writing data and to avoid data corruption in case of power loss. A resilient file system creates a copy of metadata to new blocks when editing the metadata (instead of overwriting the existing metadata) and links the latest copy of metadata to a corresponding file after writing data to the disk. We look at this in more detail below. However, when it comes to backups, block cloning in ReFS greatly increases the performance of backup solutions that take advantage of block cloning technology. Synthetic full backups would no longer need to move data around but instead can utilize pointers to existing blocks for the synthetic operation.
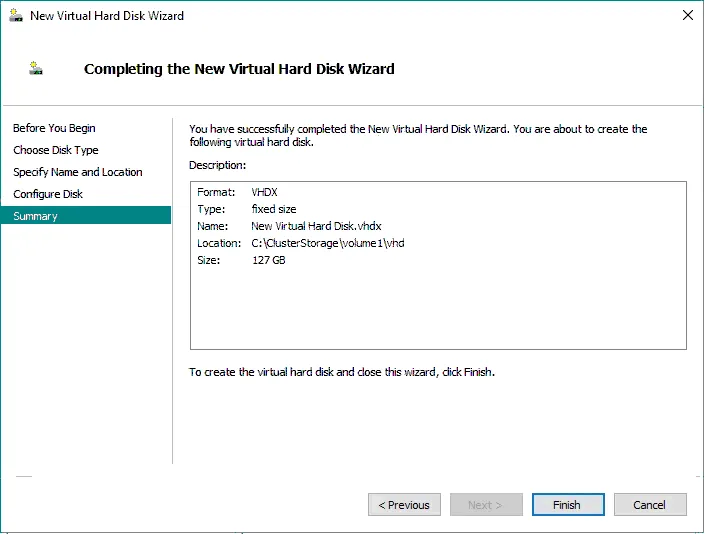
- Sparse VDL. Sparse VDL or valid data length allows ReFS to zero out files very rapidly. When creating a fixed-size VHD disk in Hyper-V, the operation could take minutes to complete to allocate the disk size. However, with sparse VDL ReFS can zero out the Hyper-V disk files rapidly. It now takes seconds to create a large fixed-size disk on a ReFS volume.
Creating the default size 127-GB fixed-size disk in a Hyper-V cluster with a ReFS clustered shared volume, shown below, took seconds. This operation would have taken minutes on a traditional NTFS formatted volume. The time to create fixed-size disks is reduced in this case.
Backup Technology Use Cases
Utilizing ReFS block cloning in modern backup solutions can yield great results. Many backup solutions that back up virtual environments use a process called synthetic full backups. Before we define a synthetic full backup, let’s consider a traditional full backup.
With a traditional active full backup of a virtual machine, all needed data is retrieved for the full backup from the production VMware or Hyper-V virtual machine itself. In doing that, essentially both the production network and storage are used to create that full backup.
With synthetic backups, the data for the full backup is synthesized from backup data that you already have in the backup repository. New full backups are synthesized, and the backup chain is moved forward. Block cloning technology with Windows Server 2019 ReFS can greatly speed up the process in which legacy backup solutions can synthesize backups due to the movement of pointers rather than the blocks themselves.
With modern backup solutions such as NAKIVO Backup & Replication, this is not required, though. VM backups are stored in the full synthetic mode. Each recovery point is aware of the blocks that are needed to fully recover a virtual machine. This means there is no need to run the transformation of backup files or recreate full backups using the synthetic process.
Windows Server 2019 ReFS Best Practices
While ReFS is certainly a remarkable file system bringing forth many improvements, are there use cases where we do not use ReFS? Yes, there are some ReFS disadvantages. Below are a few areas to note:
- ReFS cannot be used for the system drive/boot drive of the Windows operating system. In fact, you do not see an option to format your boot drive with ReFS during Windows installation, as NTFS is still the way to go for the operating system.
- ReFS supports Windows Data Deduplication starting from Windows Server 2019 1809 LTSC. If you use an older version and if you want to utilize deduplication for a Windows volume by using the native Windows deduplication capability, you need to stick with NTFS.
- ReFS does not support file-level encryption. You can use BitLocker encryption with ReFS. However, this is a volume-level encryption technology. If you want to encrypt at the file/folder level, you will need to use NTFS.
- Disk Quotas are not supported with Microsoft ReFS.
- ReFS doesn’t support short 8.3 (DOS-compatible) file names like progra~1.txt that are supported in NTFS for compatibility.
- ReFS consumes more system resources for operation. A larger ReFS array consumes more RAM, CPU resources, and disk input/output operations per second (IOPS).
- It is not recommended that you install applications on ReFS volumes. ReFS doesn’t support hard links (until ReFS v.3.5).
To take advantage of Microsoft ReFS, it is recommended that you use this server file system in the following scenarios:
- Building a file server with support of extra-large volume size and file size.
- Creating volumes to store Hyper-V virtual machines.
- Opt for ReFS on Windows servers rather than on Windows workstations.
- ReFS is preferred if you use Storage Spaces and Storage Space Direct on your server.
Note: Storage Spaces is a feature that allows you to create a virtual volume by using multiple physical disks on one computer. Storage Spaces support mirroring like RAID 1.
Thoughts
The features included in Windows Server 2019 ReFS greatly benefit environments with resiliency, scalability, and performance improvements. Now you know the advantages of ReFS, the limitations, and when you should not use this file system. The 3.4 version of ReFS has advantages in some aspects but is not a direct replacement for NTFS. You can store Hyper-V VMs on ReFS volumes to get better results but don’t forget about Hyper-V backups.
Download the Free Edition of NAKIVO Backup & Replication to protect your Hyper-V environment. The NAKIVO solution supports synthetic backup with encryption and compression. Using the ReFS file system by following the best practices and the NAKIVO solution allows you to achieve the best results.