Backup as a Service (BaaS) Benefits for MSPs
Cloud services are popular nowadays and many organizations use the cloud to store data and run virtual machines (VMs). Data stored on-premises and in the cloud should be backed up. For this reason, cloud providers provide backup as a service (BaaS) for organizations wishing to outsource data protection. This blog post explains what backup as a service is and how BaaS can help protect an organization’s data.
What Is Data Backup?
Data backup is the process of creating copies of data, machines, or files and storing these copies in a separate location and on a different medium from the original data source. The main purpose of data backup is to ensure the retention and availability of data in case of accidental deletion, hardware failures, data corruption, cyberattacks, natural disasters, or other unexpected events that could lead to data loss and downtime.
Data backup is a critical component of data management and cybersecurity. It should be part of any organization’s disaster recovery strategy and data management practices to ensure data availability and resilience in the face of unexpected events. Data backup can be classified into different categories. The main backup types in terms of how data is written are full, differential, and incremental.
What Is Backup as a Service (BaaS)
Backup as a service (BaaS) is a cloud-based service model that provides organizations with a streamlined and outsourced solution for data backup and recovery. With BaaS, instead of managing their own backup infrastructure, software, and processes, organizations rely on a third-party service provider’s infrastructure and expertise to back up their data to remote cloud storage. BaaS offers several benefits, including ease of use, scalability, and reduced operational overhead.
BaaS is particularly popular among small and medium-sized businesses and remote or distributed teams because it offers an affordable and efficient way to protect critical data without the need for extensive IT resources. It also provides peace of mind knowing that data is securely stored in the cloud and can be easily restored when needed. Users select a BaaS provider carefully based on factors such as data security, compliance, recovery options, and pricing to ensure that the service aligns with their specific needs and requirements.
Why BaaS is important
BaaS is important to reduce the risk of data loss. Large organizations can afford to build on-premises backup infrastructure for local resources and hybrid cloud, but not all small organizations can do that. In this case, small organizations can use backup as a service, which is reliable and affordable for them.
Backup as a service is important for several reasons and it plays a crucial role in ensuring data availability, resilience, and business continuity for organizations:
- BaaS helps protect data from various threats, including accidental deletion, hardware failures, data corruption, cyberattacks, and natural disasters.
- By creating backup copies of data, BaaS ensures that critical information can be recovered and restored, minimizing data loss and downtime.
- BaaS offloads the maintenance, updates, and support of backup infrastructure to backup service providers, reducing the load on in-house IT teams.
How Does Backup as a Service Work?
Backup as a service works by outsourcing the entire backup process to a third-party service provider (backup service provider), that uses cloud-based infrastructure and software to back up and protect the organization’s data. The main categories and components that make it possible for BaaS to work are explained below.
- Service subscription. An organization or individual subscribes to a backup service provider’s service plan. This plan defines the amount of storage space, backup frequency, and other service-specific features.
- Initial setup. After subscribing to the BaaS service, the user typically sets up their backup preferences and parameters. This may include specifying which data, files, folders, or systems to back up, defining the backup schedule (for example, daily, weekly, etc.), and configuring retention policies.
- Agent installation (optional). In some cases, a user may need to install a backup agent on the devices or servers they wish to back up. The agent is responsible for identifying and transmitting data to the backup service provider’s infrastructure. As for virtual machines, agentless backup can be used.
- Data transfer and encryption. Data is securely transmitted over the internet from the user’s devices or on-premises infrastructure to the BaaS provider’s cloud-based storage. Encryption is commonly used to protect data during transmission and storage, ensuring its confidentiality and integrity.
- Storage in the cloud. The backup-as-a-service provider stores the backed-up data in geographically distributed data centers, offering redundancy and availability. These datacenters are equipped with strong security measures to protect data from unauthorized access and physical threats.
- Retention policies. BaaS solutions often allow users to define retention policies, specifying how long backup copies should be retained. Older backups may be automatically deleted to free up storage space in accordance with the retention policy.
- Data management and monitoring. Users can typically access a web-based management interface provided by the BaaS provider. This interface allows them to monitor backup activities, view the status of backups, manage backup settings, and initiate data restores when needed.
- Data recovery. In case of data loss, accidental deletion, hardware failure, or other disasters, users can initiate data recovery and restore data from the BaaS provider’s infrastructure. Depending on the service, users may have the option to restore individual files, entire folders, or complete systems.
- Scalability and maintenance. BaaS solutions are designed to be scalable, allowing users to adjust their storage needs as data volumes grow. The backup service provider manages maintenance, updates, and the underlying cloud infrastructure to ensure reliability and availability.
- Support and security. Backup service providers typically offer customer support and ensure data security by employing encryption, access controls, and compliance measures to protect data from unauthorized access or breaches.
- Billing and cost management. Users are billed based on the subscription plan and the amount of storage space used. Costs can vary depending on factors such as storage capacity, data transfer volume, and additional features.
Thus, backup as a service simplifies the backup process for organizations, providing a convenient and cost-efficient way to protect their data without the need for extensive on-premises backup infrastructure and IT expertise. The data is securely stored offsite in the cloud, ensuring data availability and recovery in case of unexpected events or data loss scenarios.
Types of Cloud Backup as a Service
Cloud backup as a service (BaaS) encompasses several types or approaches to data backup and recovery, each catering to different needs and use cases. These BaaS types offer varying levels of flexibility, control, and functionality. The common types of cloud BaaS are:
- File-level BaaS focuses on backing up individual files and folders. It is suitable for personal use and small businesses with relatively simple data backup needs. File-level BaaS is used for protecting documents, photos, videos, and other individual files from loss or accidental deletion. The features are easy to set up, user-friendly, and cost-effective for smaller data sets.
- Server-level BaaS backs up entire servers or virtual machines (VMs). It is often used in businesses that rely on virtualization or have critical server infrastructure. This type can be used for protecting application servers, database servers, and VMs in data centers to provide comprehensive server protection and faster recovery of complete server environments.
- Database-level BaaS is adapted specifically for backing up and recovering databases. It is essential for businesses with critical database systems. This BaaS type is used for protecting databases like Oracle, MS SQL Server, MySQL, PostgreSQL, and others. Database-level BaaS can provide granular database recovery options, optimized for databases.
- Endpoint BaaS focuses on backing up data from individual devices, such as desktops, laptops, and mobile devices. It is suitable for remote and mobile working devices. This type of backup as a service is used for protecting data on laptops, tablets, and smartphones used by employees who work remotely or travel frequently.
- Cloud-to-cloud BaaS specializes in backing up and recovering data that resides within cloud-based applications and services. It’s commonly used with cloud productivity suites like Microsoft 365 and Google Workspace. Cloud-to-cloud BaaS is useful for protecting emails, documents, calendars, and other data stored in cloud-based productivity and collaboration tools. This type ensures data resilience for cloud-based applications and helps recover data lost due to user error or malicious activities.
- Hybrid BaaS combines on-premises backup with cloud-based backup. It offers flexibility and redundancy by backing up data both locally and offsite. Hybrid backup as a service is used by businesses that require a balance between on-premises and cloud backup for compliance, performance, or data sovereignty reasons. Hybrid BaaS is focused on local backups for quick recovery and cloud backups for disaster recovery and remote accessibility.
- Archival BaaS focuses on long-term data retention and compliance requirements. It is designed to store data for extended periods, often with infrequent access. Archival BaaS is popular for compliance-driven industries like finance and healthcare or organizations with legal data retention obligations. This backup as a service type can provide cost-effective long-term data storage and data retention compliance.
The choice of BaaS type depends on an organization’s specific requirements, including data volume, recovery time objective (RTO), compliance needs, as well as the types of devices and systems used. Many BaaS providers offer a combination of these types to fit a wide range of use cases, allowing businesses to build their data backup and recovery strategies accordingly.
BaaS Payment Models
The payment model for backup as a service (BaaS) typically involves subscription-based pricing, where users pay a recurring fee for the service. Usually, the services of backup service providers are paid monthly or annually. Additionally, the pay-as-you-go pricing model can be used. The specific pricing structure can vary between BaaS providers and may depend on several factors. The common factors that can influence BaaS pricing are:
- Storage capacity:
- The amount of storage space you require for your backups is one of the most significant pricing factors. BaaS providers often charge based on the volume of data you back up.
- Pricing may tier, meaning that the cost per gigabyte decreases as you use more storage.
- Data transfer and bandwidth usage:
- Some backup service providers charge for data transfer, which includes both uploading data to their servers and downloading data for restores.
- High data transfer volumes can impact costs, especially if you need to recover large amounts of data frequently.
- Number of protected devices or users. BaaS pricing may be influenced by the number of devices, servers, endpoints, or users you want to protect. Some providers charge on a per-device or per-user basis.
- Backup frequency and retention. The frequency of backups (for example, daily, hourly, etc.) and the retention policy (how long backups are stored) can affect pricing. More frequent backups and longer retention periods may increase costs.
- Service level agreement (SLA). Some BaaS providers offer different service levels with varying levels of data availability and recovery time objectives (RTOs). Higher SLAs may come at a premium cost.
- Data compression and deduplication. Some BaaS solutions offer data compression and deduplication, which can reduce storage requirements. This may impact pricing, as less storage space is needed.
- Encryption and security features. BaaS providers may offer different levels of encryption and security features. Enhanced security options might come with additional costs.
- The number of data restores. Some backup service providers include a limited number of data restores in their base pricing, with additional restores incurring extra charges. Frequent restores can lead to higher costs.
- Geographic redundancy. If you require geographic redundancy (data stored in multiple data centers for disaster recovery), it may come with added costs.
- Support and service level. Premium support and service levels, including 24×7 support and dedicated account management, may be available at an extra cost.
- Contract length. The length of your contract or subscription can influence pricing. Longer-term commitments may offer cost savings compared to month-to-month plans.
- Additional features and add-ons. Some backup-as-a-service providers offer add-on features such as advanced reporting, compliance tools, and integration capabilities. These features may have separate costs.
- Number of backup versions. BaaS providers may allow you to retain multiple versions of backups. The more versions you retain, the higher the storage costs may be.
- Data center location and availability zones. The choice of data center location and the use of availability zones for redundancy can affect pricing, as some regions may have different cost structures.
- Volume discounts. Some BaaS providers offer volume discounts for large-scale deployments or for customers with substantial storage needs.
It’s recommended that you carefully evaluate the pricing models and terms offered by BaaS providers to ensure that they align with your organization’s data protection requirements and budget. Additionally, consider the scalability of the service to accommodate future data growth and changing backup needs. Comparing pricing and features among different backup service providers can help you make a balanced decision about the best backup-as-a-service solution for your specific use case.
Benefits of Backup as a Service
Backup as a service plays a pivotal role in enabling companies to avoid data loss while simplifying data backup procedures by relying on a managed backup cloud. BaaS additionally delivers cost efficiencies and establishes a robust foundation for data recovery. Notably, a dependable BaaS provider brings forth a multitude of advantages for organizations. Most notably, managed backup as a service eliminates the difficulties linked with the administration of backup infrastructure.
Backup as a service offers several benefits to organizations as it is adapted for the cloud. These advantages make BaaS an attractive solution for data backup and recovery needs. The key benefits of Backup as a service are:
- Simplicity and ease of use
- BaaS solutions are typically user-friendly, with straightforward setup and management interfaces.
- Users do not need to worry about configuring complex backup systems or managing hardware and software components.
- Scalability
- Backup service providers offer scalable storage solutions, allowing users to increase or decrease storage capacity as their data grows or shrinks. There is no need to worry about how to increase storage space or move data to another location.
- This flexibility accommodates changing storage requirements without overcommitting resources.
- Redundancy and data resilience
- BaaS providers can store data in geographically distributed data centers with redundant infrastructure, enhancing data availability and protection against hardware failures or disasters.
- Data redundancy ensures that multiple copies of data exist, reducing the risk of data loss.
- Automation
- BaaS solutions automate the backup process, ensuring that data is regularly and consistently backed up without manual intervention.
- Scheduled backups help reduce the risk of data loss due to human error or oversight.
- Quick data recovery
- BaaS solutions typically offer fast data recovery options, allowing users to retrieve their data quickly in case of data loss or disasters.
- This minimizes downtime and business disruption.
- Security
- BaaS providers often enable encryption during data transmission and storage, enhancing data security.
- Access controls and authentication mechanisms help protect data from unauthorized access.
- Remote accessibility
- Users can access their backed-up data from anywhere with an internet connection, facilitating remote work and data retrieval.
- This accessibility is especially valuable for businesses with remote or distributed teams.
- Compliance and data retention
- BaaS providers often offer features that facilitate compliance with data retention and regulatory requirements.
- Users can define retention policies to ensure data is stored for the required duration.
- Support and maintenance
- Backup service providers handle the maintenance, updates, and support of the underlying backup infrastructure, reducing the burden on in-house IT teams.
- Users can rely on the provider’s expertise and support resources.
- Reliability
- Reputable BaaS providers offer high levels of service uptime and data availability, minimizing the risk of data unavailability.
- These benefits make backup as a service an attractive choice for individuals and organizations seeking a convenient, cost-effective, and reliable solution for data backup and recovery, whether for personal data protection or business continuity purposes.
- Cost-efficiency
- BaaS eliminates the need for significant upfront capital expenditures on backup infrastructure, hardware, and software.
- Users typically must pay a subscription fee based on their storage needs, allowing for predictable budgeting.
- BaaS reduces the need for dedicated IT administrators to manage and maintain on-premises backup systems, potentially saving on labor costs.
- Disaster recovery preparedness. Backup as a service can be a crucial component of an organization’s disaster recovery plan, ensuring that the organization can restore the data in the event of a disaster or data loss incident.
- Reduced risk of ransomware impact. If a ransomware attack strikes, organizations can restore their data from unaffected backup copies, reducing the need to pay ransom to attackers.
- Customization and flexibility. Many BaaS providers offer customization options, allowing users to configure backup schedules, retention policies, and encryption settings to their specific needs.
BaaS Concerns
Backup as a service offers numerous benefits, but it also comes with certain concerns and considerations that organizations should be aware of:
- Data security and privacy
Dependency on internet connectivity is a concern with backup as a service because it can lead to slow backups and recoveries, potential data transfer costs, interruptions in access during internet downtime, and security considerations. This reliance on the internet may impact the speed, availability, and cost-effectiveness of data backup and recovery processes.
- Concern: Storing data in a cloud environment raises questions about data security and privacy. Users may worry about unauthorized access, data breaches, or data exposure.
- Mitigation: Choose a reputable BaaS provider that implements strong encryption, access controls, and compliance measures. Ensure that your provider adheres to data privacy regulations.
- Data transfer speed and bandwidth usage
- Concern: Uploading large volumes of data to the cloud for initial backups can be time-consuming and may consume significant bandwidth.
- Mitigation: Plan your data transfers during off-peak hours, consider using data compression, and monitor your bandwidth usage. Some backup service providers offer options for physical data transfer via shipped drives.
- Cost management
- Concern: BaaS costs can accumulate, especially as data volume grows. Users may worry about unexpected expenses.
- Mitigation: Monitor your data storage and transfer usage regularly. Understand your provider’s pricing model and any potential hidden fees. Adjust your backup strategy to minimize unnecessary storage and transfers.
- Limited control. There can be limited control when using backup as a service because the management and maintenance of backup infrastructure and data are typically handled by the backup service provider. This can restrict customization and direct control over certain aspects of the backup process.
Why Managed Service Providers Should Offer BaaS
Backup as a service is useful not only for clients but also for service providers. Managed Service Providers (MSPs) should offer backup as a service (BaaS) to expand their service offerings, create new revenue streams, enhance client relationships, improve competitiveness, and provide critical data protection solutions to businesses of all sizes, thereby boosting client retention and loyalty. As IT environments evolve, the importance of data protection is increasing. BaaS allows MSPs to adapt to changing client needs and technological advancements.
Using NAKIVO Backup & Replication as a BaaS Solution
NAKIVO Backup & Replication is a powerful all-in-one data protection solution that can be used in a multi-tenant mode by managed service providers to provide backup as a service. The NAKIVO solution supports a wide set of features to provide BaaS, including data encryption, backup to a local and cloud infrastructure, backup verification, backups with immutability, flexible retention policies, scalability, and a user-friendly web interface. There is a wide set of features that make NAKIVO Backup & Replication an attractive backup-as-a-service solution to protect physical and virtual infrastructures.
Multi-tenant mode. A Managed Service Provider (backup service provider) can deploy NAKIVO Backup & Replication in multi-tenant mode, and create accounts for multiple tenants who are clients. Each client has access only to his/her own account and environment with allocated resources. The web interface for tenants is the same as the web interface in the single-tenant mode. A managed service provider has an extended web interface for a master admin to manage tenants and the whole environment.
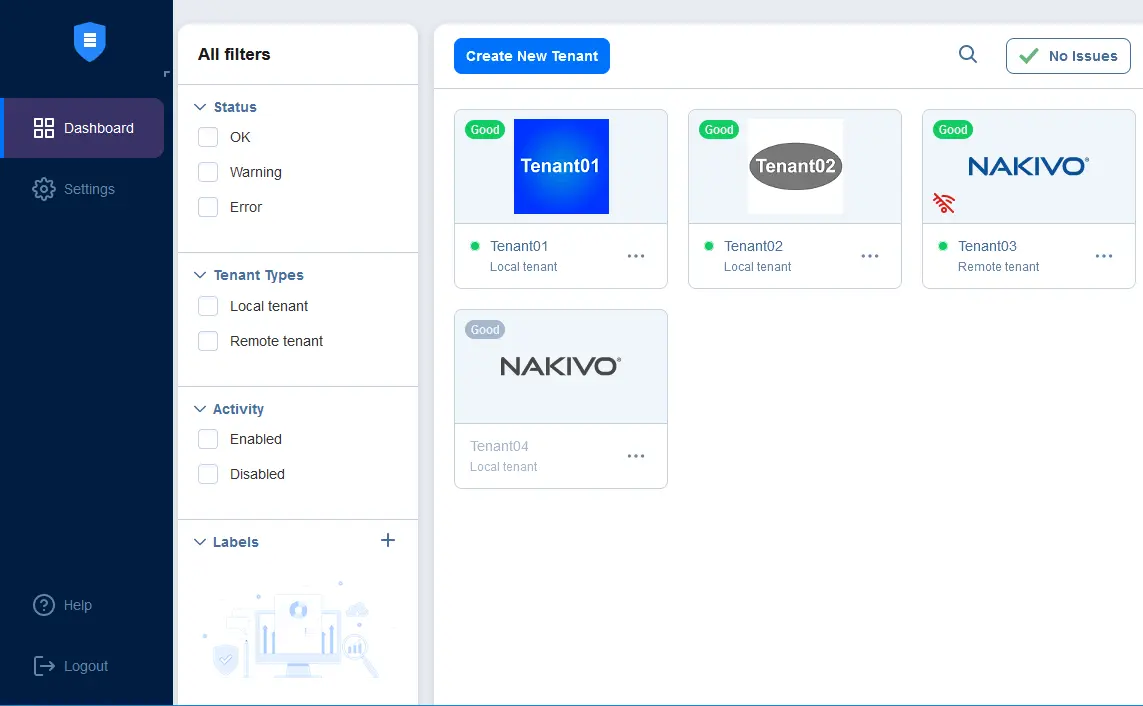
Convenient licensing principle. NAKIVO Backup & Replication is distributed in 5 paid editions that are licensed using perpetual or subscription-based per-workload licensing types. A Managed Service Provider buys licenses for the appropriate number of units, such as CPU sockets, VMs, Microsoft 365 users, physical machines, and other workloads, and delegates the needed number of workloads to each tenant from this MSP pool. Familiarize yourself with the MSP Partner Program, which gives more benefits.
Read more about possible deployment and configuration schemes for tenants to back up data between different sites.