What Is Offsite Disaster Recovery
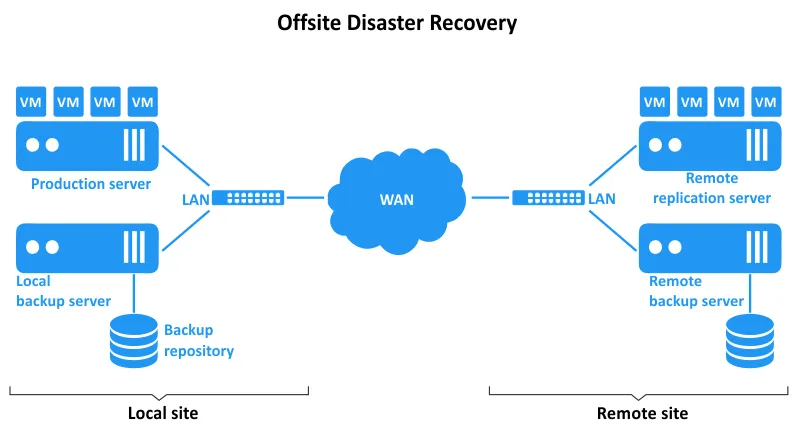
Offsite disaster recovery involves storing backup copies of data offsite in a pre-prepared infrastructure. This approach allows you to recover data and restore workloads in case of failure at the main site or if a disaster affects the main site. This is a business continuity strategy that uses data backup and replication to protect data. The data is stored away from the primary or production site, for example, away from your office or main data center.
This blog post explains offsite disaster recovery, its importance, and the working principle. We’ll also explain how to set up offsite backup and replication for disaster recovery.
How Does Offsite Disaster Recovery Work?
Storing backups and replicas away from the main environment is the foundation of offsite disaster recovery. With backups, you can save on storage requirements and other resources, which is also important when transferring data via a wide area network (WAN) or internet to a remote location. While replication is more resource-intensive but allows you to restore workloads in a shorter time.
The fundamental processes of offsite disaster recovery are offsite backup, offsite replication, and offsite data storage. Let’s explore them in more detail.
What is offsite backup?
Offsite backup is the copying of data from a production site to a secondary site located at a distance from the production site. The two sites are distributed geographically to avoid data loss if a disaster affects the first site. The offsite backup approach can be similarly implemented to back up data from a primary server to an offsite server located remotely. This operation can be part of an offsite disaster recovery plan.
The 3-2-1 rule
When planning for disaster recovery and protecting backup data, we always want to have more than one source of being able to restore our production systems. The standard recommended by industry experts is the 3-2-1 backup rule. This rule states that we should ideally have three copies of our data on two different mediums, and store one offsite copy of that backup data.
The 3-2-1 backup rule helps us diversify our backup sources so that we don’t have all of our recovery options relying on one source, medium, or backup location. This is extremely important to consider when building a data center disaster recovery plan and a backup strategy.
Recovery from offsite backups
Restoring data from an offsite backup may take more time compared to an onsite backup. But this approach significantly increases the overall reliability of the data protection strategy. A backup can be used to recover individual files.
However, if you use only offsite backups for disaster recovery, the recovery time can be too long for large amounts of data. Restoring from a backup requires time for extracting and copying the data from a backup to a server or virtual machine. To achieve a shorter recovery time objective (RTO) you can use offsite data replication.
What is offsite replication?
Offsite replication is the process of creating a point-in-time copy of data to use for failover and recovery of workloads in a short time. When replicating a virtual machine, we create a VM replica that is a VM clone of the primary VM on the secondary server located offsite. The VM replica is ready to power on and restore workloads if a primary VM fails.
The advantage of using offsite replication is the short time needed to restore workloads with the data compared to restoring data from a backup. A replica contains uncompressed data ready for use.
What is offsite data storage?
Offsite data storage is the storage located away from the primary (production) server, data center, or site with the goal of creating distributed and redundant data copies for backup and recovery purposes.
You can have an offsite backup server or an alternative storage that can store data backups and replicas and should be accessible if a disaster affects data on the primary site. There are three main destination storage types:
- A local server in a remote office or data center
- Sending backup data and replicas to the cloud
- Recording backup data to hard disks or tape and transporting these storage media to a remote location
You can build a secondary site away from your primary production center. There are three types of disaster recovery sites:
- Hot site. The infrastructure is ready for data recovery and workload failover in a short time. Minimum configuration operations are required during a disaster as everything is done in advance.
- Warm site. There is some pre-installed hardware. However, some actions are still required to configure the infrastructure before recovering data from backups and running critical workloads.
- Cold site. The preparedness level of the infrastructure is low. Only main infrastructure elements are ready. You may need to buy additional hardware with other equipment and configure servers before you can restore data from offsite backup storage and run workloads.
Reasons to Implement Offsite Disaster Recovery
Considering common disaster recovery scenarios, losing an environment in a location due to hardware failure or perhaps unintentional data loss comes to mind. Although losing a site as a result of a natural disaster or a large-scale ransomware attack may seem unlikely, being unprepared for these types of disaster scenarios can push a company out of business due to financial and brand reputation repercussions. Businesses today must prepare for any disaster recovery scenario, including losing an entire physical location.
If ransomware corrupts the main copy of data on production servers, the local backups can also be affected. Having backups in an isolated location, which is not accessible by the production network allows you to recover from a ransomware attack faster and without negotiating with hackers.
Storing replicas and backups offsite can help you if a natural disaster like fire, typhoon, earthquake, tornado, or hurricane destroys your production servers at the main site. You can restore data from the offsite backup or boot the replica in another location. Of course, in this case, the secondary site should be located far enough so as to not be impacted by the same natural occurrences as the primary site.
The benefits of offsite disaster recovery are:
- Additional protection from natural disasters
- Improved backup security, securing data from malware
- Ability to restore data and workloads
- Lower probability of irretrievably losing data
- Improved operational continuity
How to Set Up Offsite Backup and Replication for Disaster Recovery
When creating an offsite disaster recovery strategy, you need to select a data protection solution to help you implement it. This solution should support backup, backup copy, data replication, and failover. Automating tasks and attaching/detaching backup destination storage is the recommended functionality.
With NAKIVO Backup & Replication, we can create VM backup, backup copy, and replication jobs which allow us to create a secondary copy of our data. We can store a copy of our backups in multiple locations, including detachable storage media, tapes, and the cloud.
Let’s explore how to set up offsite backup and replication using an example of a VMware vSphere environment and the NAKIVO solution.
Configuring a backup copy job for offsite backup
With NAKIVO Backup & Replication you can use the Backup Copy feature to create a copy from a backup stored in a local repository and send it offsite. Your backup copy data can, of course, be stored locally on another backup server on the same site. However, to achieve the full benefit of a backup copy, ideally, we would want this copy to reside in another location connected via the network, either LAN or WAN-based technologies. This way, we have a copy of our backup data that is offsite, which satisfies the last 1 of the 3-2-1 rule.
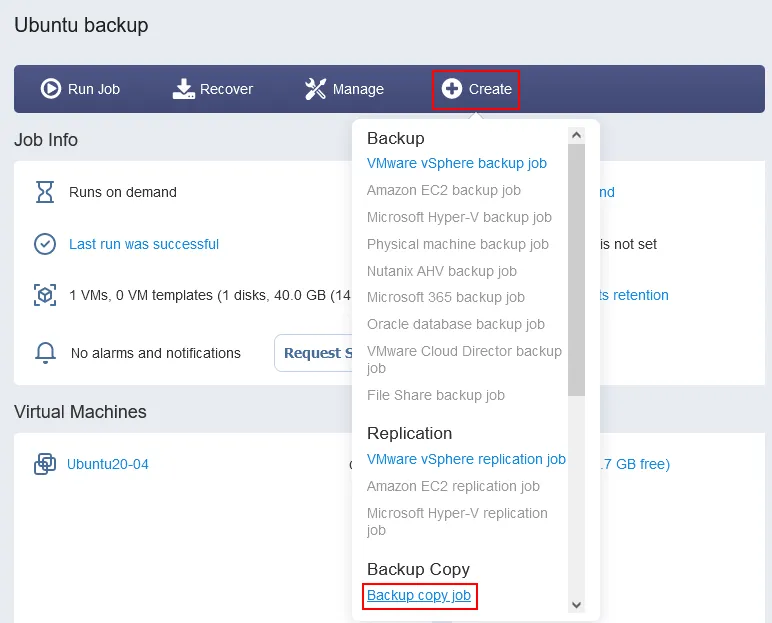
Let’s look at how to create a backup copy job in the NAKIVO solution for offsite data backup.
We need to open the web interface and click Create > Backup copy job.
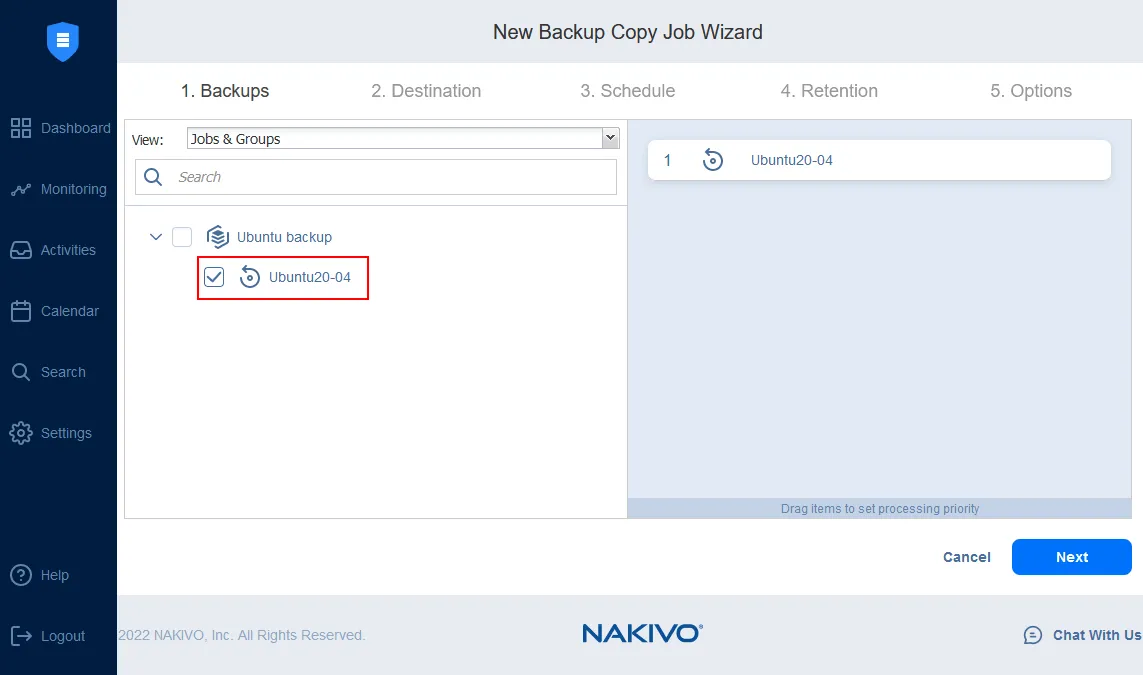
The New Backup Copy Job Wizard opens.
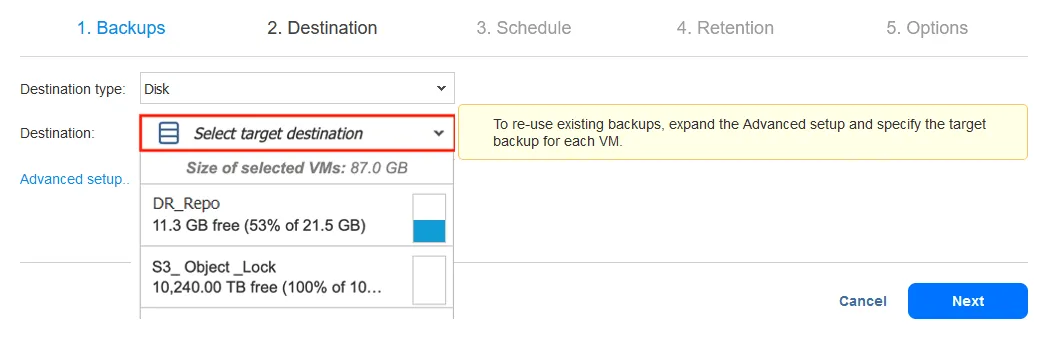
- Next is an important detail of the backup copy job configuration when we consider setting up an offsite backup location for a VM: where is the data located? Below you can choose the DR Repo, which is an offsite backup repository in the environment below.
Alternative destinations for offsite backups can be public clouds like Amazon S3 or Wasabi. Cloud repositories give you the option of enabling immutability to protect backup data against corruption and deletion by ransomware.
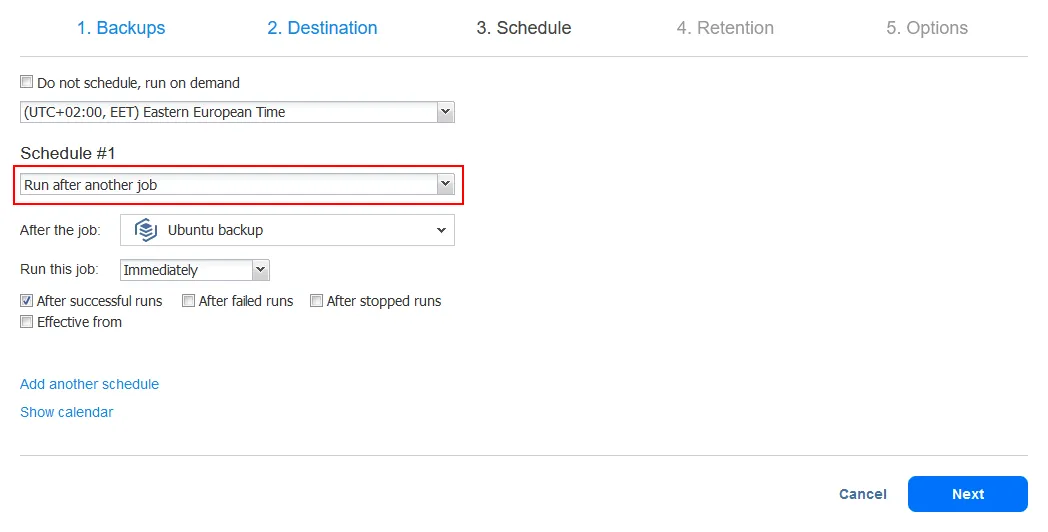
- Also, with NAKIVO Backup & Replication, we can choose to run the backup copy job immediately following a successful run of our primary backup job from production. This ensures that we always have the latest backup restore point copied over to our offsite repository.
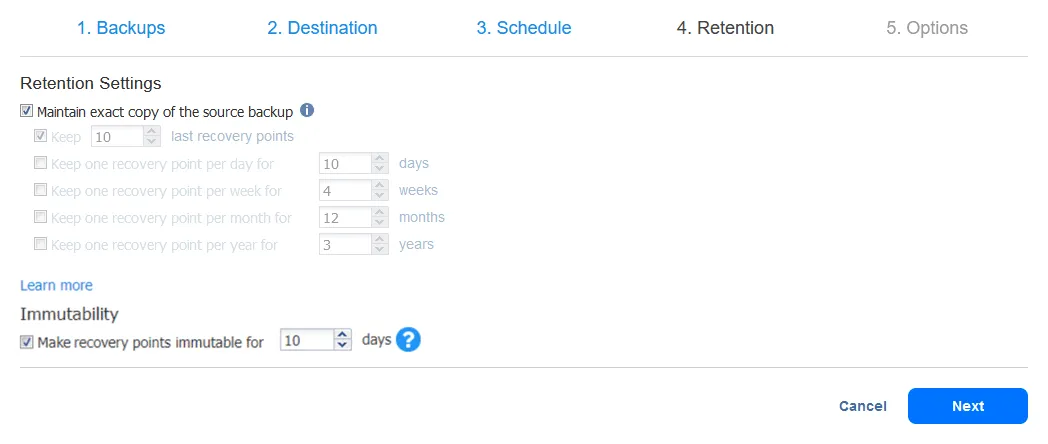
- We can select the retention period for the backup copy. As you can see below, the default is to keep the same number of points as for the source backup. When you select this option, the source backup retention policy is applied.
Note that if you choose a cloud repository or a local Linux-based repository in NAKIVO Backup & Replication, you can also enable immutability to make sure that your recovery points are protected against new ransomware infections.
- Finally, we can enable other options such as Network acceleration and Encryption, which aid in both performance and the security of data copied to the offsite backup repository.
Configuring offsite data replication
Replication allows us to create a standby replica VM for the virtual machine running in production. This standby replica VM can be onsite but ideally is stored offsite to have site failure resiliency. If we lose an entire site, we can start failover to the standby replica VM that is already provisioned in the offsite disaster recovery (DR) facility. Let’s look at how easy it is to set up a replication job in NAKIVO Backup & Replication.
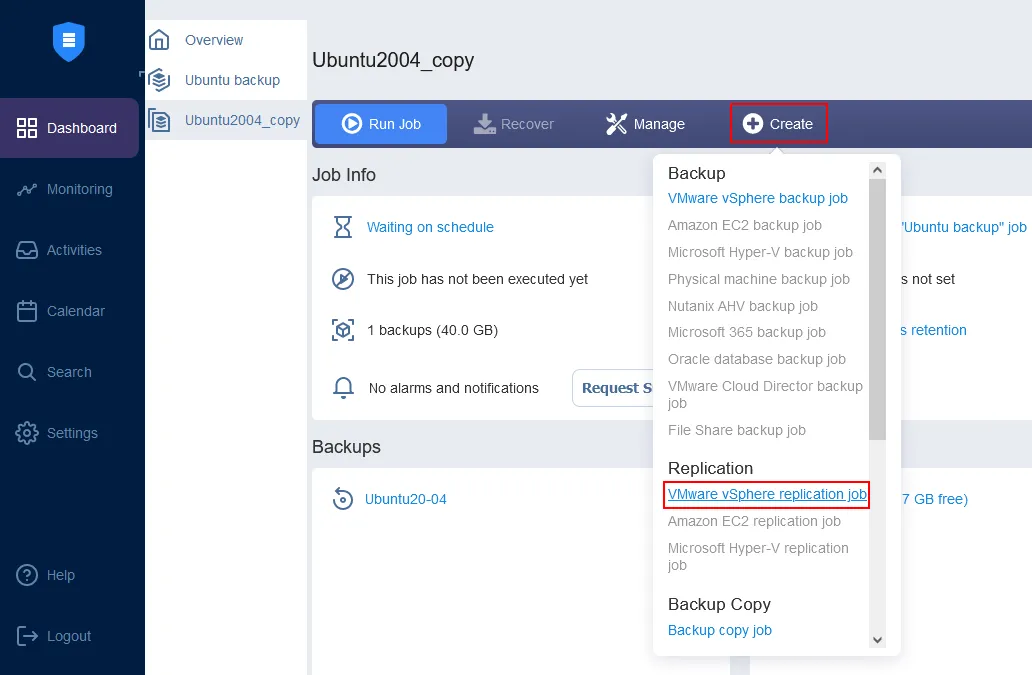
Open the dashboard, then click Create > VMware vSphere replication job.
The New Replication Job Wizard for VMware vSphere opens.
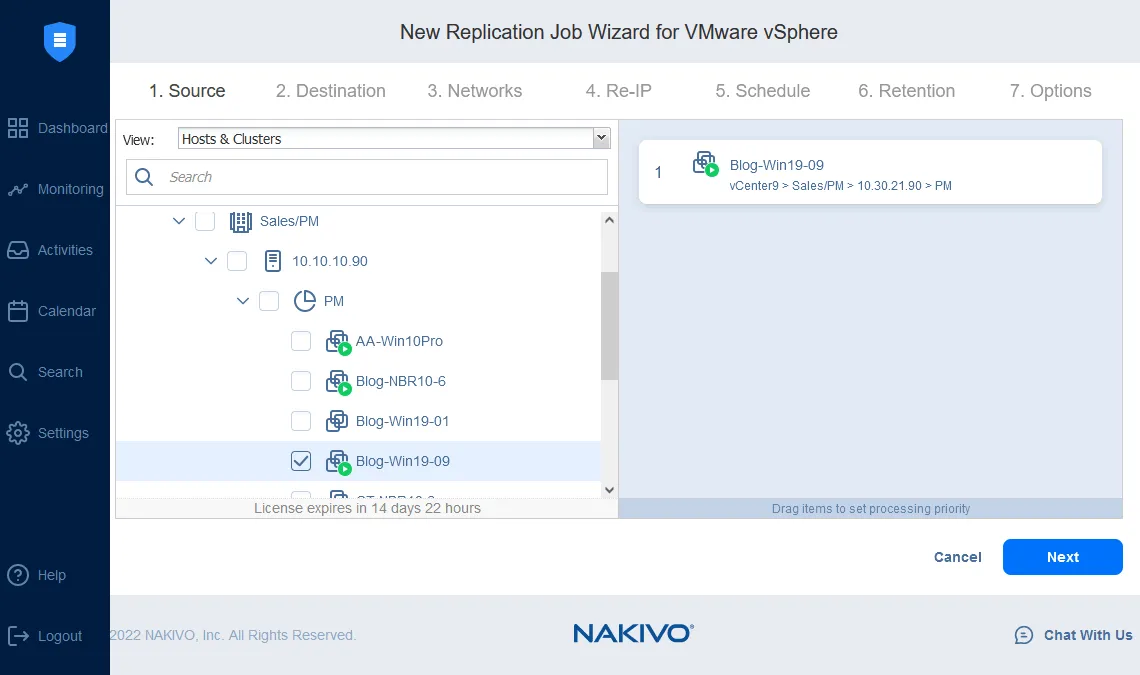
- First, select the VM that you want to replicate.
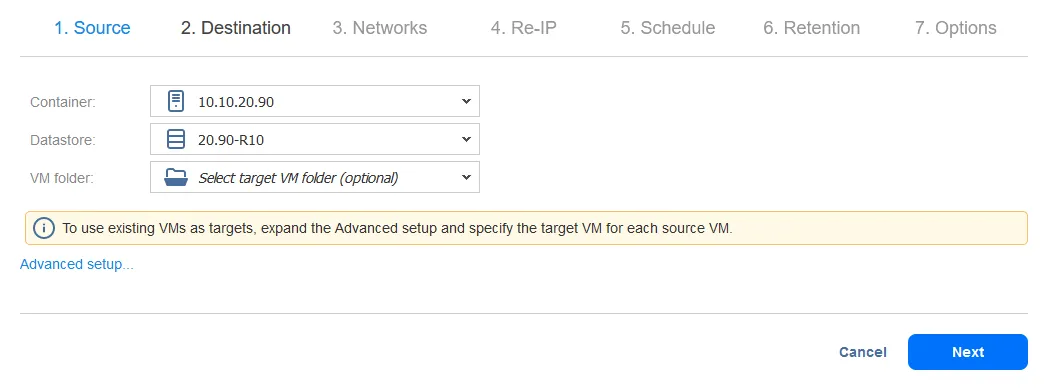
- As far as the Destination, again, the key for offsite backups and resiliency is making sure the destination VMware environment and datastore are located on a separate site.
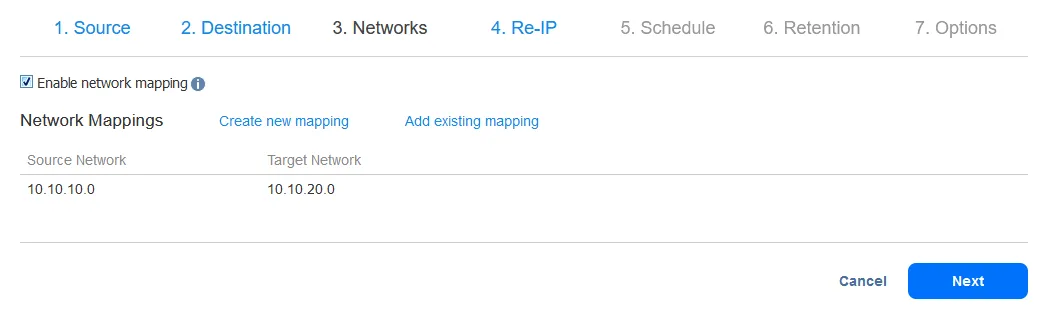
- Enable network mapping to map source VM virtual networks to appropriate target virtual networks.
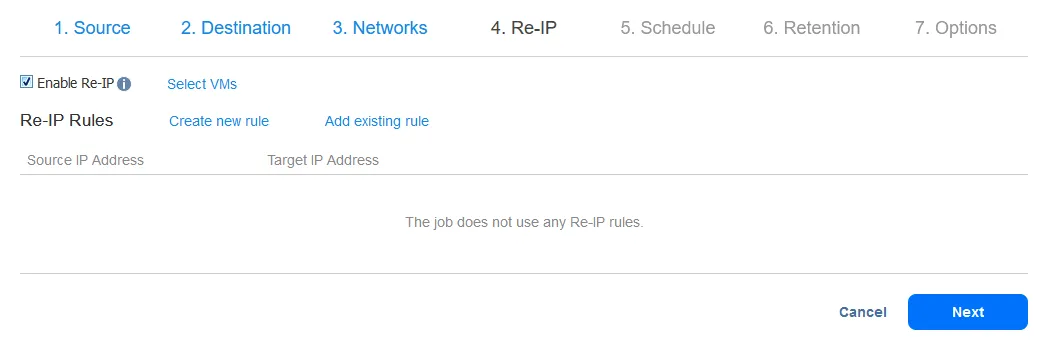
- After configuring network mapping, you can enable Re-IP to map the specific target IP addresses during recovery.
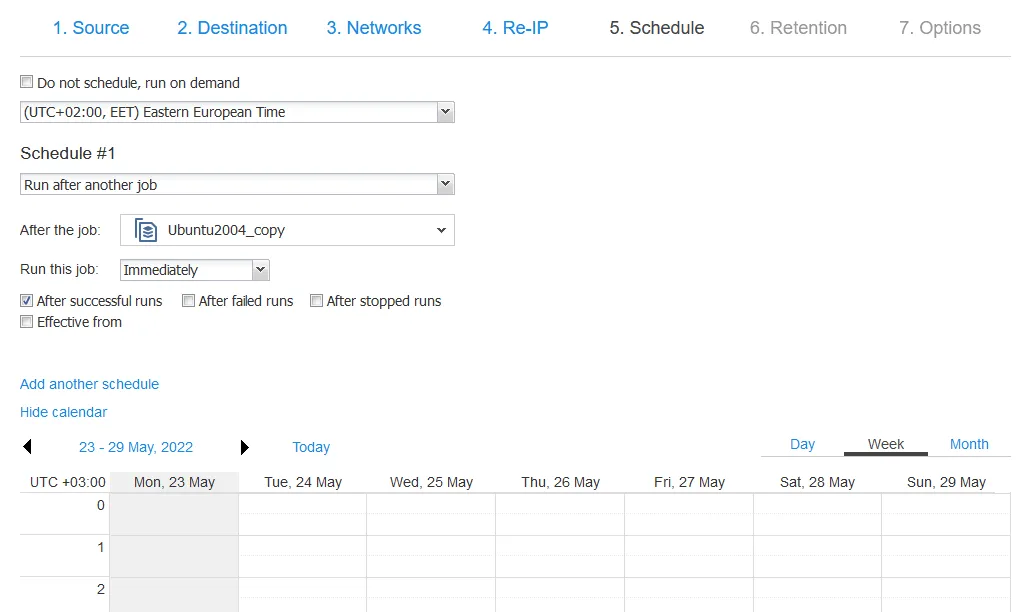
- We can schedule the replica VM to be created/updated after another job runs, such as the primary backup job. A calendar helps us see when other tasks are scheduled to avoid overlaps.
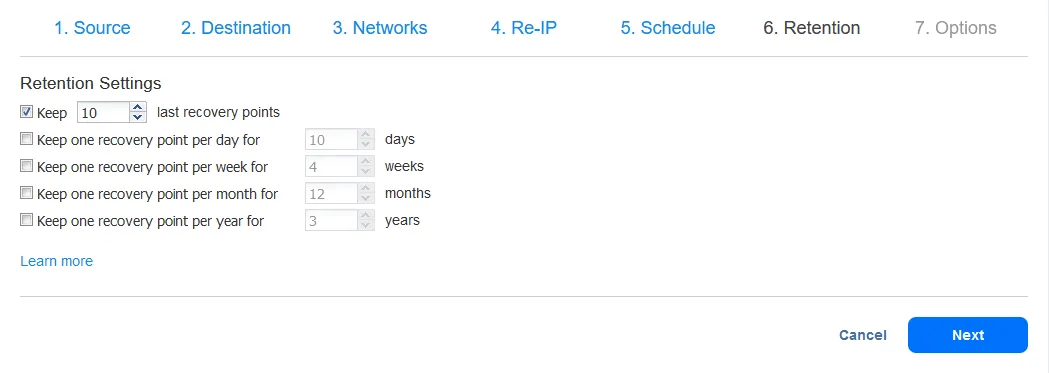
- With the retention on a replica VM, this is accomplished via a point-in-time snapshot every time the replication process runs. You can specify the number of snapshots/retention points you want to keep. The NAKIVO product supports the GFS retention scheme.
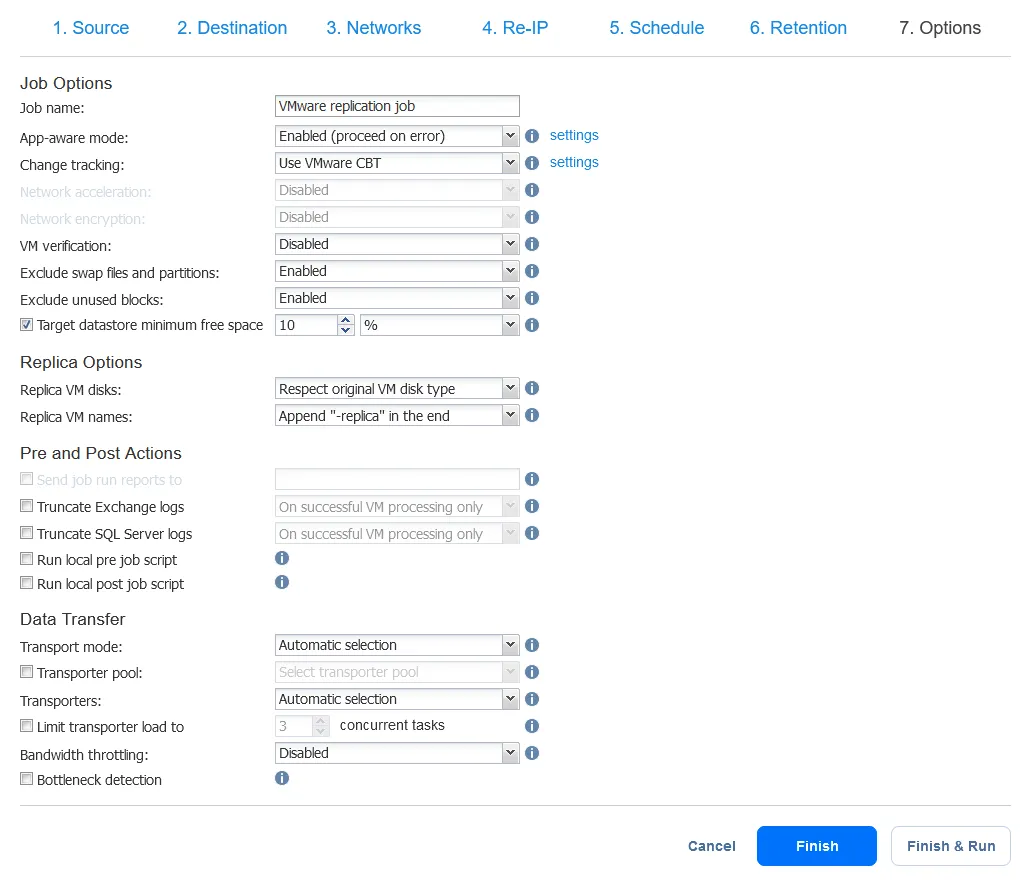
- Finally, you can choose a number of options to control the performance and security of the replication job, such as network acceleration and in-flight encryption. Here, you also name the resulting replica VM, set email options, and execute any pre- and post-job scripts.
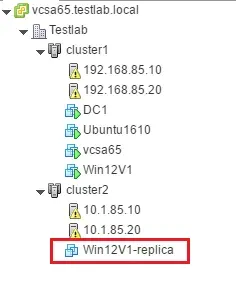
Now you know how to configure a VMware replication job for offsite disaster recovery. The VM replica is created in an offsite VMware vSphere environment. In the screenshot below, we can see an example of a local cluster on the production site and a remote cluster that is located in a DR facility.
Pro tip. The NAKIVO solution also includes a Site Recovery feature to automate workflows with data backup, replication, and test failover for disaster recovery scenarios.
Thoughts
An offsite backup and offsite replication are important parts of a disaster recovery strategy that significantly increase the probability to recover data. This approach matches the 3-2-1 backup rule to avoid a single point of failure and avoid losing data due to affecting an onsite backup. Offsite backups help to protect us from a site-wide failure resulting in both production data losses but also potentially backup system data loss.