How to Back up Microsoft 365 Apps and Services
Most cloud services today are available to customers based on what is known as the “shared responsibility model”. This applies to Microsoft 365 services and apps. Although Microsoft 365 data is stored in the cloud, this user data should be backed up by the customers. This blog post explains why you should back up Microsoft 365 data, backup features, challenges, and how to back up Microsoft 365 effectively.
Why You Should Back Up Office 365
Given that Microsoft 365 data is stored in the cloud, it may seem, at first glance, that there is no reason to back up this data. But this is a misconception.
It is true that Microsoft creates redundant copies of data between its servers and datacenters to ensure that it can provide uninterrupted services without downtime (operation continuity) and its platform is available to customers. If one server fails, other servers with redundant data can be used for failover.
However, Microsoft operates under a shared responsibility model in the cloud, whereby Microsoft is responsible for the infrastructure’s uptime and availability. The customer, on the other hand, is responsible for data protection. This means ensuring data integrity, backup, and the ability to recover from data loss incidents falls on the users of Microsoft 365 services.
What all of this means is that Microsoft has a reliable infrastructure with data redundancy and excellent failover options. But this won’t help customers and organizations to restore deleted data that was not caused by issues in Microsoft’s datacenters. Microsoft is not responsible for data loss caused by the customer’s side.
The reasons for Office 365 data loss include:
- Accidental or intentional deletion of data by Office 365 users and customers.
- Data that was finally purged after the limited retention period ended.
- Ransomware infection that corrupts data on user computers and cloud storage drives such as OneDrive mounted on infected computers.
- Bad actors delete all data of compromised (hacked) user accounts.
Other reasons why it is important to implement regular Office 365 backup:
- Regulations and compliance that require that organizations retain data and ensure data integrity for a specified period of time
- A backup provides more capabilities for faster and more effective recovery
- Native recovery options, such as Microsoft’s two-stage recycle bin provide limited functionality in durability and flexibility
- Microsoft cloud services are extremely reliable. However, in case of service disruptions or outages, having a backup can help your organization maintain smooth operations and avoid downtime.
Given all the threats to data in the cloud as well as the requirements for audit and compliance for organizations, backing up Office 365 apps and services becomes a critical component to ensure data availability, integrity, and compliance with regulations.
What Microsoft 365 App Data Should Be Backed Up
Microsoft 365 services operate with different types of data. Some data types are unique for each application, and some data can be used by multiple Microsoft 365 applications. This factor impacts the approach to Office 365 backup for each individual service or application.
Office 365 Exchange Online
Microsoft 365 provides Exchange Online for administration users’ mailboxes and Outlook Online for individual email use by users. Users can use the web interface of Office 365 or an email client installed in the operating system. If a user uses an email client, a local copy of email messages is stored on the disk device of a local computer (for example, in PST files). This copy can be considered as an Office 365 email backup, but not all users use installed email clients.
In the case of relying on online applications, it is more effective to back up the mailboxes of all users of Outlook Online centrally. Moreover, a user can delete a message in a web interface and email client without the ability to restore it with available tools. As for the web Outlook Online application, the deleted emails are purged no later than a month after deletion. Having a centralized Office 365 email backup can help. You should also note that emails may have complex structures, including attachments, calendar invites, and nested email threads. Capturing all elements comprehensively can be challenging. Remember that when choosing a Microsoft 365 email backup solution.
Office 365 OneDrive Backup
OneDrive is the Office 365 storage service that allows users to store data in the Microsoft public cloud and mount this cloud storage as a drive to a Windows computer. A data copy on a local disk drive and in the Microsoft 365 cloud can be synchronized. If a user deletes a file from a local computer, this file is also deleted in the cloud storage and vice versa. The same thing happens in the case of a ransomware attack. As a result, files stored in OneDrive can be lost. Some users might confuse synchronized OneDrive with a backup, but this is another misconception.
Users can recover deleted files from the native Recycle Bin in the Microsoft 365 OneDrive cloud service using versioning and eDiscovery. However, the maximum retention period for deleted files is about three months. You can read more about how to back up and recover OneDrive files with native Microsoft tools.
Users store a vast array of file types in OneDrive (for example, documents for Word, Excel, PowerPoint, etc.), including version histories and shared documents that may have unique permissions. Take into account this information when choosing a Microsoft 365 backup solution for OneDrive.
Office 365 SharePoint Backup
Microsoft SharePoint Online is an Office 365 service for collaboration, allowing users to create internal websites and upload content for other users. SharePoint Online is one of the most complex Microsoft 365 apps to back up because it contains many data types, and this data can be interdependent.
When it takes to Office 365 backup for SharePoint Online, consider a backup of the following types of data, depending on the priorities of your organization:
- Site collections. Entire site collections should be backed up to ensure all content, configurations, permissions, and settings are preserved. This includes both team sites and communication sites.
- Documents and libraries. Back up all documents, files, and items stored within document libraries across site collections. This includes versions of documents and metadata associated with files.
- Lists and list data. Capture the data and configurations of SharePoint lists, including custom lists, calendars, tasks, announcements, contacts, and more.
- Site configuration and settings. Back up site settings, such as site themes, site templates, site columns, content types, site navigation, and custom scripts.
- Site permissions and security. Ensure that user permissions, groups, and security settings are backed up to maintain access controls and compliance requirements.
- SharePoint app data. If your organization uses SharePoint apps or add-ins, ensure that app data and configurations are backed up to maintain functionality and integrations.
Keep in mind these types of SharePoint data when choosing a backup approach for SharePoint Online in terms of Office 365 backup. Native tools to recover SharePoint Online data, similar to OneDrive, include a Recycle Bin (up to 93 days), versioning, retention policies, and eDiscovery. You can use them in certain situations, but their functionality is limited compared to a true backup copy.
Office 365 Teams backup
Microsoft Teams includes chats, files shared in chats or teams, meeting recordings, notes, and more. The diverse data types and the interconnectedness between Teams and other Microsoft 365 services complicate the backup process:
- Chat Messages
- Teams and Channels
- Posts and Conversations in Channels
- Files and Documents
- Meeting and Call Records
Teams integrates closely with other Microsoft 365 applications like SharePoint Online, OneDrive for Business, and Exchange Online. Data related to Teams is not stored in a single location – instead, it is spread across these services. For example, files shared in Teams are stored in SharePoint or OneDrive, whereas chat messages are stored in the Azure cloud. This dispersed data storage model complicates the backup process.
Native Microsoft 365 backup and recovery tools allow you to back up and restore Microsoft Teams data in some way:
- Backup options in the Security & Compliance Center for OneDrive
- Teams policies in the Microsoft Teams admin center
- Backup options for Exchange Online for meeting data
- Retention and messaging policies for chat messages and conversations
Microsoft 365 Native Data Protection Options
Microsoft 365 native backup and recovery options are limited, as you can see from the explanation for each service backup option. The options include:
- The two-stage recycle bin
- Versioning
- Retention settings and litigation hold
- eDiscovery
These tools aren’t true backup tools but rather retention policies that help keep deleted items longer. They lack the flexibility and reliability of a dedicated backup solution.
The granularity is limited when it comes to restoring specific items or versions. There are no long-term retention capabilities. There is a limit to version histories and time-bound recovery from the Recycle Bin, which might not meet all your needs. Limitations in time and functionality of native Microsoft 365 backup and recovery options can lead to considering advanced data protection solutions for Office 365 backup.
Challenges of Microsoft 365 Data Protection
Microsoft 365 backup and recovery is not easy, and there is a set of challenges:
- Data stored across apps and services. Microsoft SharePoint and Teams interact with OneDrive. Microsoft Teams data types also use SharePoint, OneDrive, and Exchange. Different data types are scattered across different Office 365 services, and backing up this Office 365 data can be challenging.
- Limitations of native backup tools. Native tools offer item-level recovery and retention policies rather than true backups. There’s no straightforward way to perform a complete, point-in-time recovery of the data you need.
- Lack of a centralized view of all data and users. Native tools for Microsoft 365 backup and recovery can be configured from different locations. You need to check different options in different Microsoft 365 admin centers, such as Exchange Online admin center, SharePoint Online admin center, Teams admin center, etc. Native backup and recovery options are scattered across different pages. Accessing, configuring, and managing them can be challenging.
- Low control of data recovery. When using native tools, the options of what to recover and where to recover are limited. The recovery points in time are limited. If you send an official request to Microsoft for recovery of everything, you cannot select what to recover, and some latest data written before a failure can be lost.
- The restore time. The recovery time of Office 365 data with native tools can be high due to the large number of manual operations. If you request Microsoft to recover all data for the appropriate point of time, the time to process your request is required and there is no option to select what to restore.
Microsoft 365 Backup with NAKIVO Backup & Replication
To address the challenges of Microsoft 365 backup and recovery, consider using a dedicated data protection solution instead of native Office 365 tools that are not fully functional data protection tools. NAKIVO Backup & Replication is a universal data protection solution that includes advanced tools to back up and recover Microsoft 365 data.
The advantages of protecting Microsoft 365 with the NAKIVO solution:
- Support for the main services: Exchange Online (users and groups), OneDrive for Business, SharePoint Online, and Teams.
- Point-in-time restores. You can configure where to back up data and the time intervals, and automate the Office 365 backup process.
- Flexibility and better visibility into data across platforms. You can manage the data of all Microsoft services to protect in a single centralized interface.
- Local storage. The advantage of storing Office 365 backups on local storage is the ability to access them and restore data if internet connection issues occur or if remote cloud services are down.
- Advanced recovery options. You can recover specific Microsoft Office 365 objects to the original location (the source Office 365 user) and to the custom location (another Office 365 user) or save selected Office 365 objects to your local computer. The recovered objects can be Outlook email messages, OneDrive files, etc.
- Better RPO and RTO. You can back up data more frequently and recover faster. The backup process is automated.
The NAKIVO solution uses APIs provided by Microsoft to access the Office 365 data of Microsoft 365 cloud services, which makes backup and recovery processes convenient.
How to configure Office 365 backup with NAKIVO
Configuring Office 365 backup with NAKIVO Backup & Replication is straightforward. To start, follow the steps below:
Add Microsoft 365 to the inventory
Add your Microsoft 365 organization account to the inventory as the SaaS item. You can select which Microsoft 365 services to protect or you can select all services.

Create a backup repository for Microsoft 365 backups
- Create a directory on the machine with the installed Transporter (on the machine where you are going to store Office 365 backups). Ensure that there is enough free space on the disk where the backup repository will be located. Configure the required permissions to access the directory where a backup repository will be located by NAKIVO Backup & Replication.
- Create a SaaS backup repository in the web interface of the NAKIVO solution. Select the Transporter and define the directory where to create the new backup repository.

Create a backup job
- Click + and click Backup for Microsoft 365 to create a new Office 365 backup job in the web interface of NAKIVO Backup & Replication.
- Select the needed Office 365 items in the first (Sources) step of the New Backup Job Wizard for Microsoft 365. You can select entire organizations, groups of items or specific mailboxes, OneDrives, SharePoint sites and Teams. Hit Next at each step of the wizard to continue.

- Select a destination backup repository where to store Office 365 backups – the SaaS backup repository you created earlier.
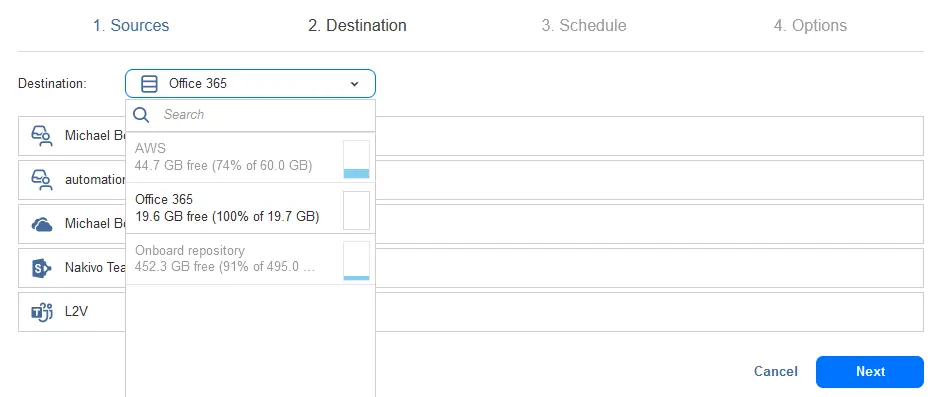
- Configure scheduling settings. You can create multiple schedule rules to implement flexible schedule and retention schemes.

- Configure Office 365 backup job options. Enter a job name, select the priority, mailbox processing options (if you’ve selected a mailbox in Sources step), including backup for In-Place hold/archive items, litigation hold items, calendar and contacts, etc., and other options. Click Finish & Run to save settings and run the backup job immediately. Alternatively, you can click Finish and wait until a scheduled job will be run automatically.

- Select the job run scope and check how long to keep recovery points. Hit Run to start the backup job.

The recovery process is also straightforward. You should go to Jobs > Recover > Object Recovery for Microsoft 365 in the NAKIVO web interface and complete the recovery wizard.





