VMware Horizon and VDI: Key Differences Explained
Virtualized servers running on virtual machines (VMs) are widely used by companies in production environments. They offer several advantages, including scalability and cost-efficiency. In certain scenarios, using virtualized desktops can also provide multiple benefits. This blog post explores virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI) and its use cases. We will also cover VMware Horizon as well as the solution’s features and use cases.
What Is VDI?
Virtual Desktop Infrastructure (VDI) is a technology that allows users to host a desktop operating system (OS) on servers. In addition, VDI also allows users to access VM-based desktops remotely from different devices and locations. VDI can be deployed in a private or public cloud, and it is considered a type of IaaS (infrastructure as a service). This means that IT service providers can provide DaaS (desktop as a service).
VDI vs VM
VDI relies on virtual machines (VMs) to provide virtual desktops. A virtualization server contains multiple VMs and each VM can be used to provide a virtual desktop and run applications for users.
When to Use VDI
VDI can be used as an alternative to traditional infrastructures in which actual physical desktops are used. There are some use cases for which a virtual desktop infrastructure is especially handy:
- Remote work: Users can access their virtual desktops from anyhwere via a device with an internet connection.
- BOYD: For employees that use their own devices for work, VDI can enhance security by separating work workloads on centralized servers and by helping minimize the risk of unauthorized access.
- Scalability: VDI allows for quick provisioning of new desktops and easily add/remove users as needed.
- Ease of administration: VDI can help organizations avoid the issues associated with using different hardware for physical desktops (for example, finding or installing different drivers) as well as simplify software updates (updating on virtual desktops is much easier).
- Cost: Organizations can save on buying new workstations and buy only new servers. VDI can alos provide cost savings by reducing hardware and maintenance costs.
What Is VMware Horizon?
VMware Horizon, or VMware Horizon View, is a solution from VMware for deploying a virtual desktop infrastructure, and it integrates fully with VMware’s product line. VMware Horizon is based on VMware vSphere and uses the vSphere environment for hosting virtual desktops. User desktops are VMs running on ESXi hosts. Hence, vSphere features such as snapshots, vMotion, High Availability, Distributed Resource Scheduler, and others are available.
As of early 2023, VMware vSphere 8.0 and VMware Horizon 2106 are the latest available versions.
VMware Horizon VDI vs. terminal services
VMware Horizon works differently from terminal servers such as VNC or Windows Terminal Services (previously known as Remote Desktop Services). The VMware Horizon VDI solution provides greater flexibility and security than terminal services because user data is stored on virtualized servers that can be managed, updated, and backed up centrally. Users can connect to virtual desktops through personal computers (PCs), tablet PCs, smartphones, thin clients, or zero clients.
On the other hand, when using terminal services, users can access the server and use applications in their own sessions according to permissions specified by the administrator(s). One physical server or virtual machine is shared by multiple users, and access to local resources may be restricted for them. Some software may not work properly with remote desktop services.
Notes
- A thin client is a low-cost computing device that has low-performance hardware – typically just enough for the connection to the server.
- A zero client, an ultrathin client that forms part of a client-server model, is a small box with an attached keyboard, mouse, and monitor. It has a network interface and provides the ability to use these devices as if you are connected to the server directly. A zero client has no storage capacity.
When to Use VMware Horizon
Since VMware Horizon is a VDI solution, it can be deployed for any of the use cases listed above in this article. If you are using the VMware vSphere virtualization platform, using VMware Horizon can be especially advantageous.
VMware Horizon can be used in a variety of scenarios:
- Remote work – to provide remote access to virtual desktops and applications for employees working from home or other remote locations.
- Branch and remote offices – to provide virtual desktops and applications to employees in branch and remote offices without the need for local infrastructure.
- High-performance computing – to deliver virtual desktops with high-performance graphics capabilities for users who need to run demanding applications, such as video editing or 3D modeling.
- Bring your own device – to help organizations support a bring your own device policy by delivering virtual desktops and applications to employees’ personal devices while keeping data secure and separate from personal information.
VMware Horizon is also used by many IT service providers (including MSPs) to provide virtual desktop infrastructure (VDI) services to clients. MSPs often use VMware Horizon because it offers a range of features and capabilities that can be tailored to meet the needs of clients. VMware also provides a partner program that is designed specifically for MSPs, which includes training and support resources to help MSPs build and manage VDI solutions using VMware Horizon.
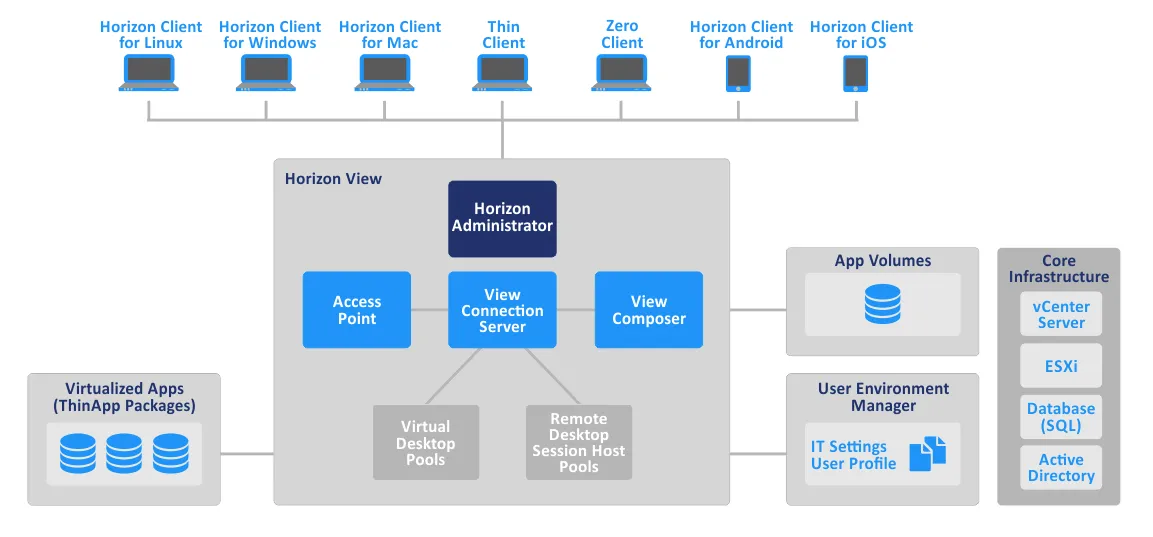
VMware Horizon Components
The main components of VMware Horizon are:
- vCenter Server is a centralized management system for VMware vSphere. vCenter can be deployed on a physical or virtual machine. However, deployment on a VM running on an ESXi host is preferred, as the advantages of virtualization are available in this case. vCenter can be deployed as vCenter Server Appliance from a preconfigured OVA template.
If possible, avoid using existing vCenter servers in your vSphere environment for VMware Horizon. Deploying new vCenter servers, especially for VMware Horizon, is recommended for licensing purposes – a Horizon license includes a license for vCenter.
- ESXi Hypervisor is a physical server that hosts virtual machines. Operating systems and applications are installed on virtual machines, which function as desktops for users. ESXi hosts are managed with vCenter Server.
- View Agent is a software component that should be installed on any VM to be used as a virtual desktop and all VMs that will be managed by VMware Horizon View. This service provides connection monitoring, USB support, virtual printing, and single sign-on.
- Horizon Client is an application installed on a user’s machine to communicate with View Connection Server (see below). It establishes a connection between endpoint user devices and Horizon virtual desktops or applications. The client can be installed on Windows, Linux, and MacOS operating systems.
- Horizon View Connection Server is a server that authenticates users through Active Directory, provides single sign-on, associates virtual desktops with users, etc. The LDAP (Lightweight Directory Access Protocol) database that is used for Active Directory authentication is copied to the View Connection Server. This is one of the core components of the VMware Horizon virtual desktop infrastructure.
- ThinApp is an optional component that is used for application virtualization by VMware. This virtualization tool is agentless, so nothing needs to be installed on a user’s machine to run it.
- View Composer is used for managing virtual desktops on vCenter Server and provides rational storage consumption by using linked clones. Rather than creating full clones, linked clones are created from a parent virtual disk (VMDK). Linked clones use special differencing virtual disks to store the unique data that differs from the data on a parent disk. Linked clones don’t work without their parent disks. You can save from 50% to 90% of your storage space by using this technology. View Composer should be installed on each instance of vCenter Server separately.
- Horizon Administrator is the web interface for Horizon VDI management. It is recommended to use a dedicated Horizon Administrator instance for each instance of a Horizon Connection Server. The VMware Horizon View Administrator portal allows you to add vCenter Server and View Composer instances to your View configuration.
Connecting to Virtual Desktop and Applications with the Client
VMware Horizon Client is an application that allows users to connect to VMware Horizon virtual desktop from their devices remotely. Horizon Client is developed for Windows, Linux, Mac OS, iOS, and Android operating systems. When users enter their credentials in the Horizon Client, the application communicates with the View Connection Server to authenticate them. After authentication by Connection Server, the server finds the appropriate virtual desktops for the users and provides access to them with defined permissions.
Special remote display protocols are used to provide interaction between the end user’s device and the virtual desktop. Horizon Client supports connection via VMware Blast, Microsoft RDP (Remote Desktop Protocol), and PCoIP (PC over IP) protocols. VMware Horizon supports only Blast – a special TCP-based protocol developed by VMware. A PNG/JPG-based codec is used for delivering graphic and video data.
In Horizon 7.0, VMware released Blast Extreme, which allowed HTML access with a browser (this protocol can also be used for access from v4.0 or later of the Horizon client). In addition to a PNG/JPG-based codec, Blast Extreme can use the H.264 video codec. The most suitable of these codecs is selected automatically depending on the conditions.
Connection from HTML-5 compatible browsers is especially useful for clients who cannot install the Horizon Client on their device.
Users of zero-client devices should use PCoIP if these devices are designed especially for using this protocol and don’t support VMware Blast.
Thin clients must have the VMware View client installed. Visit the VMware compatibility guide page to see which thin clients can run the VMware View client. Follow the user manuals in order to configure thin clients.
VMware Instant Clone Technology and Master Desktop Templates
VMware View Composer includes a cloning option that you can use to create linked clones. Before creating linked clones, you should create a Master Desktop Template. To clarify, let’s first define some of the terms.
A clone is a copy of an existing virtual machine called the source VM or parent VM. Two types of clones are usually used in virtual environments: full clone and linked clone.
- A full clone is an exact reproduction of the parent VM, which doesn’t share any VM components with the parent VM. A full clone is not dependent on the parent VM during operation. The performance of a full clone is the same as the performance of its parent VM. All data is copied from the parent VM to the VM clone in this case.
- A linked clone is a VM copy that shares the virtual disks of the parent VM. This allows you to save storage space and time spent on clone creation. A linked clone is dependent on the parent VM and cannot function if the parent VM is missing or is not reachable. A snapshot of the parent VM is made to create each linked clone. Differencing virtual disks (delta disks) are created after the snapshots are made. Changes to the virtual disk of the linked clone don’t affect the virtual disk of the parent VM and vice versa.
Instant Clone, introduced with VMware Horizon 7, is the technology that allows you to create clones near-instantly. This is achieved by providing rapid in-memory cloning of a parent VM in a running state and using the copy-on-write approach. As a result, clones are created rapidly and without affecting the parent VM.
Instant clones share the memory and disks of the parent VM. When a file of the VM clone is about to be changed, a copy of that data is first created, and then the changes are written to the copy of the data. Hence, all modifications made with clones are isolated from the parent VM. When a snapshot is created, the VM is momentarily frozen and a delta disk is created (VMware Tools must be installed on the VM).
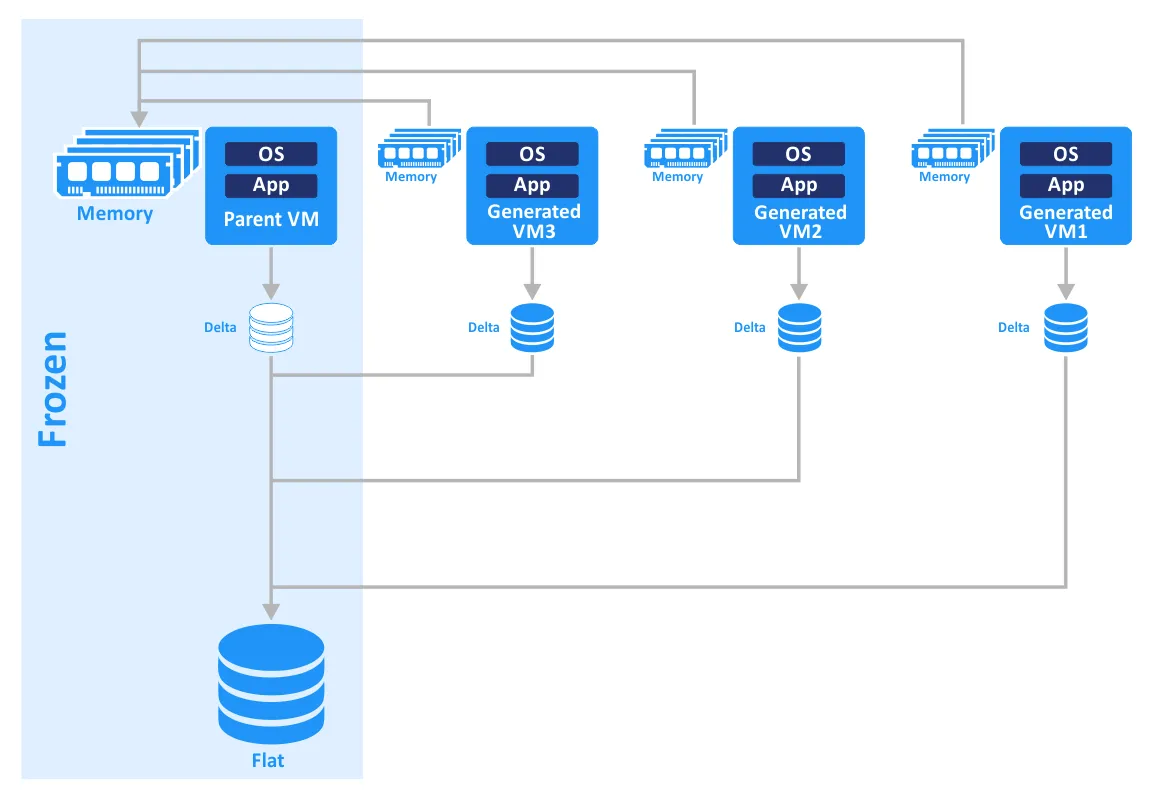
VMware Instant VM Clone Technology, also known as vmFork, ensures just-in-time desktop delivery. This technology is especially useful for the purposes of providing users with virtual desktops in VMware Horizon VDI. Creating instant clones is faster than using View Composer to create linked clones, as you don’t need to perform time-consuming Refresh, Recompose, and Rebalance actions to update and refresh virtual desktops for users. A desktop can be created in a few seconds.
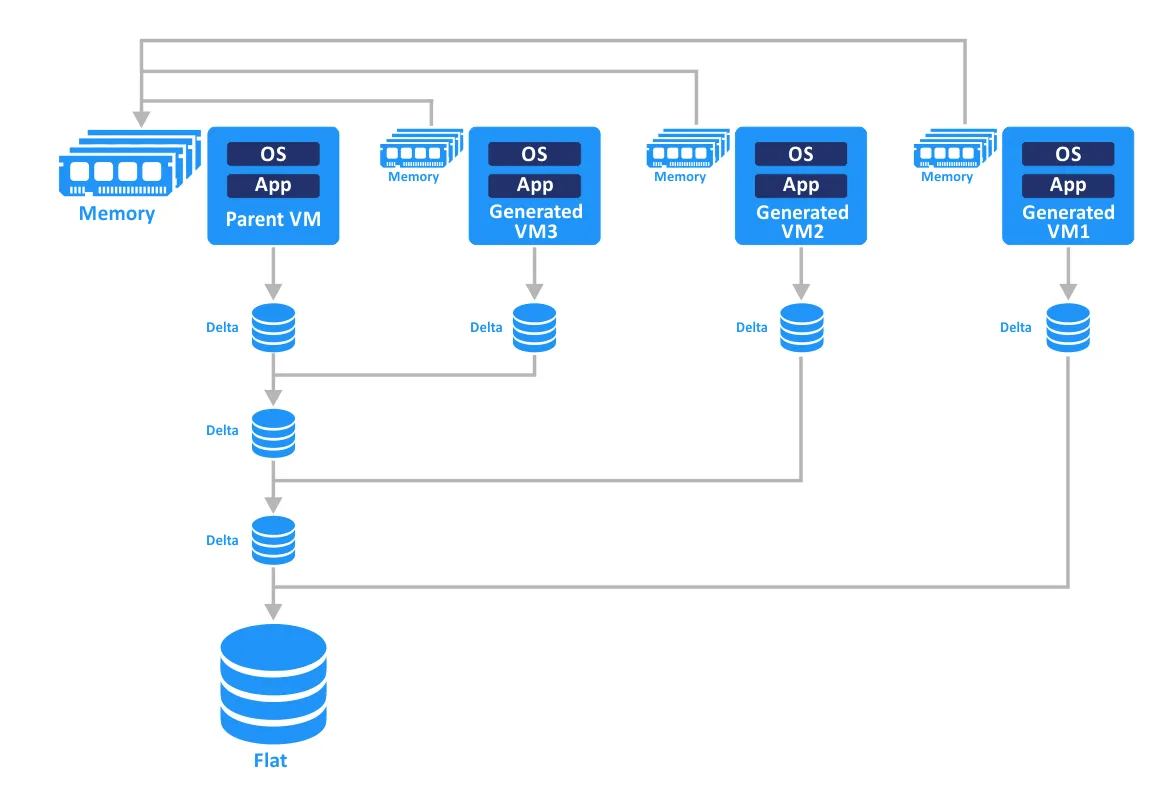
Let’s compare the sequence of actions for creating a linked clone with View Composer vs. using Instant Clone technology. Overall, creating a linked clone takes about 5-8x longer than creating an instant clone.
| Step | View Composer Clones | Instant Clones |
| 1 | Cloning | Cloning with vmFork |
| 2 | Reconfig | Power On |
| 3 | Power On | Customize |
| 4 | Customize | User Login |
| 5 | Snapshots | |
| 6 | Power On | |
| 7 | User Login |
With vSphere 6.7, Instant Clone technology was significantly improved. Instant clones no longer have such tight dependencies with their parent VMs as before. New instant clones use delta disks, but the process differs from the snapshot technique used for linked clones. The new method allows you to get around disk chain length restrictions (previously, maximum 32 snapshots were supported in a chain). Instant clones now can be created not only from a frozen parent VM but also from a running VM, which helps speed up the process.
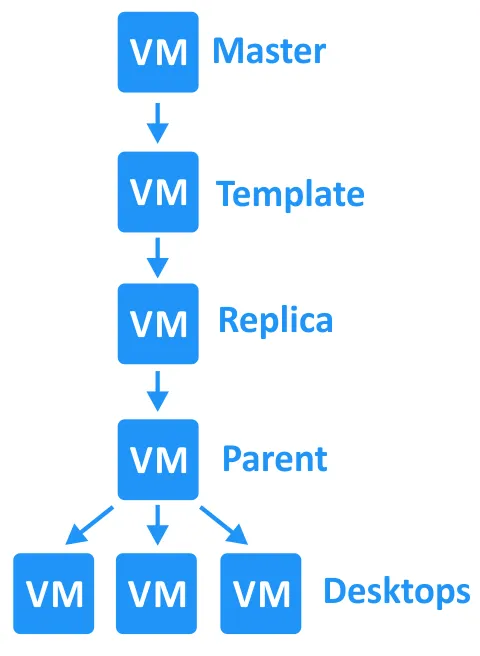
A master desktop template is a preconfigured virtual machine that is used as a base for cloning and creating VMs for virtual desktops. Using master desktop templates makes creating virtual desktops more convenient and allows you to save time.
The main steps for creating a master desktop template are the following:
- Create and configure a new VM in vCenter using VMware vSphere Client. Remove any unnecessary devices, such as floppy drives.
- Install and configure a guest operating system (OS). Configure the default user profile in the OS. Install and configure the needed software.
- Install VMware View with the VMware Horizon Instant Clone Feature.
- Install the VMware User Environment Manager Agent with the Flex Engine component (if needed). This component allows you to apply policies created by an administrator with the User Environment Manager Management Console. The Environment Manager Agent is a profile management tool that captures user settings for OS and applications specified by the administrator.
- Run the VMware OS Optimization Tool for use with VMware Horizon. This tool disables unnecessary services to improve performance. The provided templates can be customized.
- Clean up the virtual disk and then zero out the free disk space. Learn more about how to zero out disk space in our blog post on thin and thick provisioning.
- Clone the newly configured VM with VMware vSphere client.
- Use this VM clone to create a base image for further VDI desktop cloning. There are two procedures for putting the VM into a frozen state, depending on the cloning method. For full-clone desktop pools, the master VM is cloned to a VM template. For instant clone desktop pools, a snapshot of the master VM is created.
Desktop Pools: Persistent and Non-Persistent
When provisioning virtual desktops, you should create desktop pools. Desktop pools allow you to create and manage virtual desktops flexibly. There are two approaches to provisioning virtual desktops when creating desktop pools: using non-persistent desktops and using persistent desktops.
A non-persistent virtual desktop is used when all changes made by a user with the desktop must be discarded after the user logs off or the VM reboots. This is also known as floating user assignment. In this case, a user is not assigned to any specific desktop because all desktops in the pool are identical and created from one master desktop template. This type of provisioning makes sense in cases where users all need a standard application set for their working tasks and do not need to save changes after their work or install new applications.
Example. Employees at a call center or staff of a financial department use the appropriate set of applications, and the results of their work, such as call recordings or financial transactions, are saved to the company’s servers. Some users may need access only to browser applications. There is probably no need to provide dedicated persistent virtual desktops for them. Using non-persistent virtual desktops allows you to save storage space on your servers (rational consumption of computing resources) and provides more centralized management, which improves security. Different virtual desktops are assigned to users after each login.
A persistent virtual desktop is used when each user must have their own desktop with a personalized user profile and specific applications. This is also known as dedicated user assignment. After the user logs off or the VM is rebooted, the data is retained on the virtual desktop. This type of provisioning should be applied whenever users need to modify their working environments during the working process.
Example. Software developers or testers need to install new applications, update frameworks, and change their configurations regularly. In this case, choosing persistent virtual desktops is the right choice because it is much more convenient for the users. Persistent virtual desktops are also created from the master desktop template but are not recreated each time the way non-persistent virtual desktops are. A user logs onto the same virtual desktop each time.
Advantages of Using Horizon as a VDI Solution
VMware Horizon View is a VDI solution that is integrated into VMware vSphere. This makes deploying VDI more affordable for companies who already have vSphere-based virtual infrastructure and use VMware VMs. Horizon VDI supports Active Directory integration and connection to Windows Terminal Services.
VMware vMotion and vSphere clustering features, such as Distributed Resource Scheduler, High Availability, and Fault Tolerance, are also available. Unlike traditional VDI or remote desktop solutions, VMware Horizon allows for more rational consumption of resources such as storage space, CPU, memory, and networking. The solution also improves scalability, reliability, and compatibility.
What Is AVD?
Windows Virtual Desktop (WVD) is Microsoft’s solution for a virtual desktop infrastructure, first released in 2019. It is a desktop and app virtualization service that runs on the Azure cloud platform environments using Azure virtual machines. In September 2020, Microsoft rebranded Windows Virtual Desktop (WVD) to Azure Virtual Desktop (AVD).
With AVD, users can access a virtualized Windows desktop environment from any device, anywhere, and at any time. The service offers features such as multi-session Windows 10, Office 365 ProPlus optimization, and support for Remote Desktop Services (RDS).
AVD Components
The components of Azure Virtual Desktop are:
- Host Pools. A host pool is a collection of Azure VMs that share the same configuration and allow users to connect to a remote desktop or application. You can create multiple host pools to support different user groups, applications, or environments.
- Workspace. The Azure Virtual Desktop workspace is a logical grouping of resources, including host pools, application groups, and user assignments. It provides a central place for administrators to manage and configure the Azure Virtual Desktop environment.
- Application Groups. An application group is a collection of applications that can be accessed by users. You can publish individual applications or entire desktops to users, depending on their needs. Multiple application groups can be created to provide different levels of access or functionality.
- Azure Active Directory. Azure Virtual Desktop integrates with Azure Active Directory (AD) to manage user identities, access, and authentication. You can use Azure AD to create and manage user accounts, group memberships, and access policies.
- Gateway. Azure Virtual Desktop uses the Remote Desktop Gateway service to secure and control user access to virtual machines and applications. The Remote Desktop Gateway acts as an intermediary between the user and the virtual machine, ensuring that connections are authenticated, authorized, and encrypted.
- Load Balancer. The Azure Load Balancer distributes incoming traffic across multiple virtual machines in a host pool to ensure high availability and performance.
- Management Tools. Azure Virtual Desktop provides several management tools to help administrators deploy, configure, and monitor the environment. These include the Azure portal (a web-based graphical user interface), PowerShell cmdlets, and REST APIs.
As Azure Virtual Desktop is deployed only in the public cloud, administrators do manage everything, and Microsoft manages the underlying infrastructure:
| Components managed by Microsoft | Components managed by the administrator |
|
|
VM Cloning
To clone VMs in Azure for using a clone in AVD, you can use Shared Image Gallery, which is the only available cloning method. This method allows you to create a generalized image of a virtual machine, which can then be used to create multiple virtual machines. The image can be stored in an Azure Shared Image Gallery, which provides a central location for storing and managing images.
The Advantages of AVD
The list of AVD advantages includes:
- Integration with other Microsoft products. AVD is well integrated with Office 365, Azure Active Directory, and Windows.
- Enhanced security. AVD supports conditional access and multi-factor authentication to help protect against security threats.
- Cost-efficiency. AVD is billed on a per-user, per-hour basis, allowing organizations to pay only for what they use.
VMware View vs Microsoft VDI
Let’s look at a comparison of VMware Horizon View and Microsoft’s VDI solution.
| Feature | VMware Horizon | Azure Virtual Desktop |
| Deployment Options | On-premises, Cloud, Hybrid | Cloud |
| Virtualization Technology | VMware vSphere | Microsoft Azure (based on Hyper-V) |
| Management | Horizon Console, vCenter Server, PowerShell (PowerCLI) | Azure Portal, PowerShell |
| Client OS Support | Windows, macOS, Linux, Chrome OS, Android, iOS, Web (HTML 5) | Windows, macOS, iOS, Android, Web (HTML 5) |
| Application Delivery | Remote Applications, Published Desktops | Remote Applications, Published Desktops |
| Performance | High-performance, GPU acceleration, Blast Extreme Protocol | High-performance, GPU acceleration, RemoteFX Protocol |
| Integration with Other Products | vSAN, NSX, Workspace ONE, vRealize Operations | Office 365, Microsoft Endpoint Manager, Azure Active Directory, Microsoft Cloud App Security |
| Cost/Pricing | Per-user subscription, perpetual license | Per-user subscription, consumption-based |
| Release date of the first version | 2009 | 2019 |
Below we go into a more detailed VMware Horizon vs. Microsoft VDI comparison:
Deployment
VMware Horizon can be deployed on-premises or in the cloud, including in AWS and Azure. In contrast, Azure Virtual Desktop (or formerly Windows Virtual Desktop) is a cloud-only service that runs exclusively on Azure. You can deploy a VMware virtual environment in a public cloud but you cannot deploy AVD on-premises on local physical servers. The VMware Horizon VDI solution is more flexible in this respect.
Management and administration
VMware Horizon management tools are Horizon Console, vCenter Server, and PowerShell (PowerCLI). Azure Virtual Desktop can be managed with Azure Portal and PowerShell. VMware Horizon has a more extensive and flexible management and administration toolset than Azure Virtual Desktop. Horizon allows you to manage desktops, applications, and user profiles from a single console. Horizon offers features like App Volumes for delivering applications and User Environment Manager (UEM) for managing user settings. In contrast, Azure Virtual Desktop has more limited management and administration tools.
User experience
Both solutions provide excellent user experience, but some users may prefer one over the other. VMware Horizon provides better graphics performance, which is important for users who work with graphic-intensive applications. On the other hand, Azure Virtual Desktop has seamless integration with Microsoft products like Microsoft 365, which can provide a more consistent experience for users who work primarily in a Microsoft ecosystem. So the choice in this category can depend on software you use in your environment.
Licensing
VMware Horizon licensing is based on a perpetual license model, where you purchase a license and own it indefinitely. In contrast, Azure Virtual Desktop licensing is based on a subscription model, where you pay for the service on a per-user, per-month basis. The VMware solution can be more attractive if you prefer to buy a license once and forget about payments for a long time. VMware Horizon licensing includes a support subscription for the defined period.
Security
Both solutions offer robust security features, but Azure Virtual Desktop has the advantage of being a Microsoft service, which means it is deeply integrated with Microsoft security tools like Azure Active Directory and Microsoft Defender. On the other hand, VMware Horizon can be integrated with VMware NSX with wide security capabilities, including the firewall.
Both solutions are effective and can be used to deploy VDI. Your choice will depend on factors like your infrastructure, management requirements, user preferences, and preferred licensing model.
Conclusion
VMware Horizon View is a VDI solution that combines the advantages of virtual desktop infrastructure with those of the VMware vSphere virtualization platform. If your company is interested in VDI and you already use VMware virtualization products, VMware Horizon is ideal. Azure Virtual Desktop can be an optimal choice if you want to have the maximum level of integration with other Microsoft products such as Azure and Office 365. AVD can be deployed only in Azure.
Remember to back up all workloads and data in your infrastructure. NAKIVO Backup & Replication is a full data protection solution for different types of environments, including for VMware and the VMs used for virtual desktops.





