Image-Based vs. File-Based Backup Comparison
In today’s data protection landscape, there are numerous backup types that you can use to safeguard your data. When it comes to backing up separate files, many organizations rely on file-based backups and file sync solutions such as Dropbox, Google Drive and OneDrive. However, they are not the optimal choice since these types of solutions cannot ensure data recovery in case of data loss or corruption.
Image-based backup is a modern backup approach designed for today’s business IT infrastructures. It provides comprehensive data protection for the entire operating system, including files and other application data, and simplifies recoveries.
Image-based and file-based backups are used to achieve different goals. Although some may think that the two methods can be used interchangeably, a good understanding of each can help strengthen an organization’s data protection strategy. This post details the similarities and differences between the two methods.
What Is File-Based Backup?
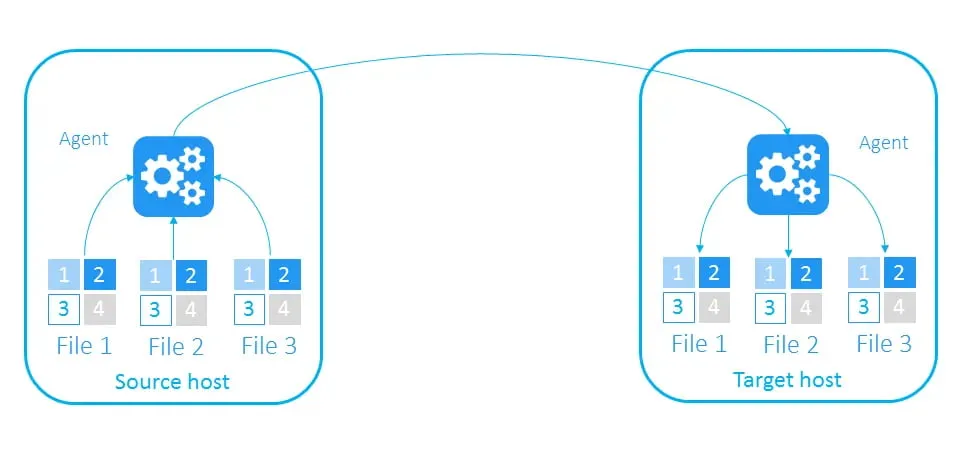
File-based backups are copies of individual files and folders. This backup approach operates at the file-system level to process source files. File-based backups work well when you generate and store a relatively small amount of data, especially if this data is platform-independent.
However, to perform file-based backups, you usually need a piece of software called an agent on the source computer and another copy of the agent on the target host (whether it is a home PC or a server in the cloud).
When you need to back up a complete system, such as a whole OS or a virtual machine, a file-based backup is not enough. An operating system, whether installed on a physical machine or on a virtual machine, is more complex than just a set of files. Operating systems contain many running operations, like data stored in RAM or input and output operations.
Note: Technically, it is possible to back up the operating system using the file-based backup method because the configuration of the OS is stored in files. However, while you are copying the content of one file, another one might be changed. Thus, even if all of the files from a source VM are copied, the backup will not be crash-consistent, complicating the recovery process later.
When it comes to the backup of operating systems and virtual machines, image-based backup is the better and more reliable option. Let’s take a closer look at image-based backups.
What Is Image-Based Backup?
Image-based backup is the process of backing up an entire virtual machine or physical machine along with the operating system, configuration files and system state. The entire backup is saved as one file known as an image.
This backup is considered crash-consistent since all data is taken at exactly the same point in time relying on Microsoft’s Volume Shadow Copy (VSS) operating at the volume level (for Windows-based operating systems). Image-based backups can also be used to create application-consistent backups to simplify the recovery of data in applications like Microsoft Exchange Server, SQL Server, Active Directory and others. You can find more information in our post on crash-consistent vs application-consistent backups.
Currently, most of the image-based solutions are agentless for virtual machines, though backup of physical machines requires the use of agents. Most virtualization solutions have a built-in mechanism to take snapshots (also known as checkpoints in Hyper-V). So, backup applications usually use the snapshots made by these inner services. Let’s take a closer look at how image-based backups are created.
How image-based backup is created
The following steps are necessary to create an image-based backup:
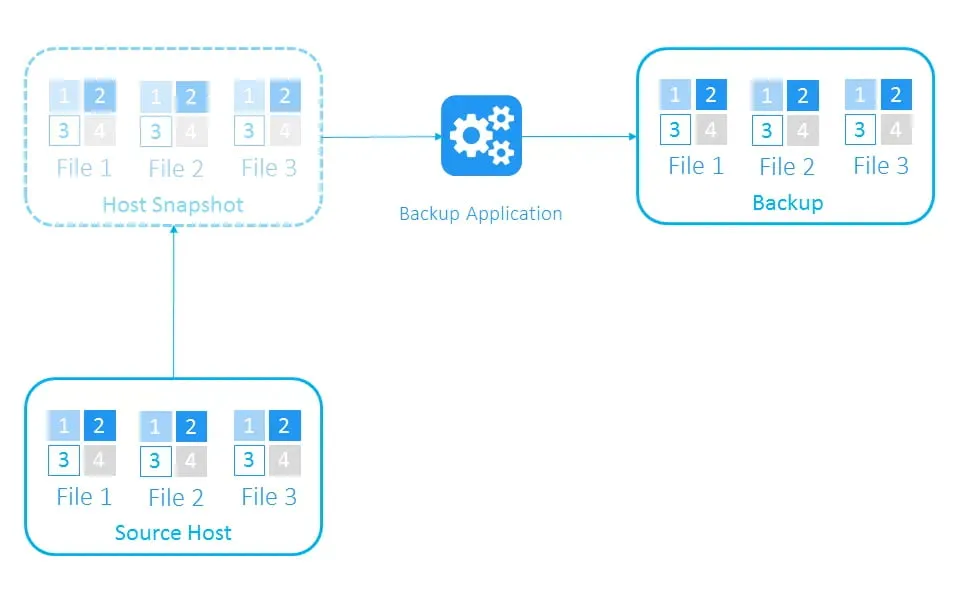
- Before a backup starts, a backup application triggers the creation of a snapshot of a VM’s disk files. This means that the state and operations are frozen at a specific point in time. VM disks switch to read-only mode, and any changes made to these disks during this time are written to delta files.
- After it creates the snapshot, the backup application copies the data from the read-only files to a backup repository while the source system continues running.
- Once the backup is created, delta files are merged into the VM disks, and VM disks resume regular write operations. The snapshot is deleted.
Advantages of Image-Based Backup
- Full machine recovery: Restoration of full machines with their operating systems and configurations for immediate use.
- Instant recovery of files and application objects: Instant recovery of different items to where they are needed for immediate resumption of workflows.
- Support for deduplication and other space-saving features
- Centralized administration of data protection: Image-based backup solutions support backup and recovery for different types of IT infrastructure from a single pane of glass.
- Automation and orchestration features: Ability to automate routine data protection activities and create automated sequences of tasks.
Image-Based Backup with NAKIVO Backup & Replication
NAKIVO Backup & Replication allows you to perform image-based, app-aware backups of Hyper-V, VMware and Nutanix AHV VMs; Amazon EC2 instances; and Linux and Windows physical servers and workstation.
Download the Free Edition of the NAKIVO solution to check out all the advanced tools and functionalities that help you ensure data recoverability and business continuity.