An Introduction to VMware vCloud Director
VMware has always released new great virtualization software for individual users, organizations, and MSPs. VMware’s virtualization products aim for an application-centric approach in data centers instead of the traditional hardware-centric approach. You can use a set of VMware virtualization solutions to build a software-defined data center. VMware vCloud Director is one of these products that can be used in large data centers. This blog post describes VMware vCloud Director main features and use cases.
What is vCloud Director?
VMware vCloud Director (VMware vCD) is a platform with multi-tenant support for managing software-defined data centers (SDDC) and providing infrastructure as a service (IaaS) to customers. This solution is adapted for managed service providers (MSPs). The IaaS provider can build a private or public cloud and use VMware vCloud Director to manage the virtual data center flexibly and efficiently.
You can create a virtual data center based on multiple physical data centers, allocate resource pools, and provide the appropriate services to customers. Then customers consume provided resources and use virtual machines residing in the data center. At the time of writing this post, the latest version of VMware vCloud Director is VMware vCloud Director 10.2 – now renamed to Cloud Director (without “v”).
How VMware vCloud Director Works
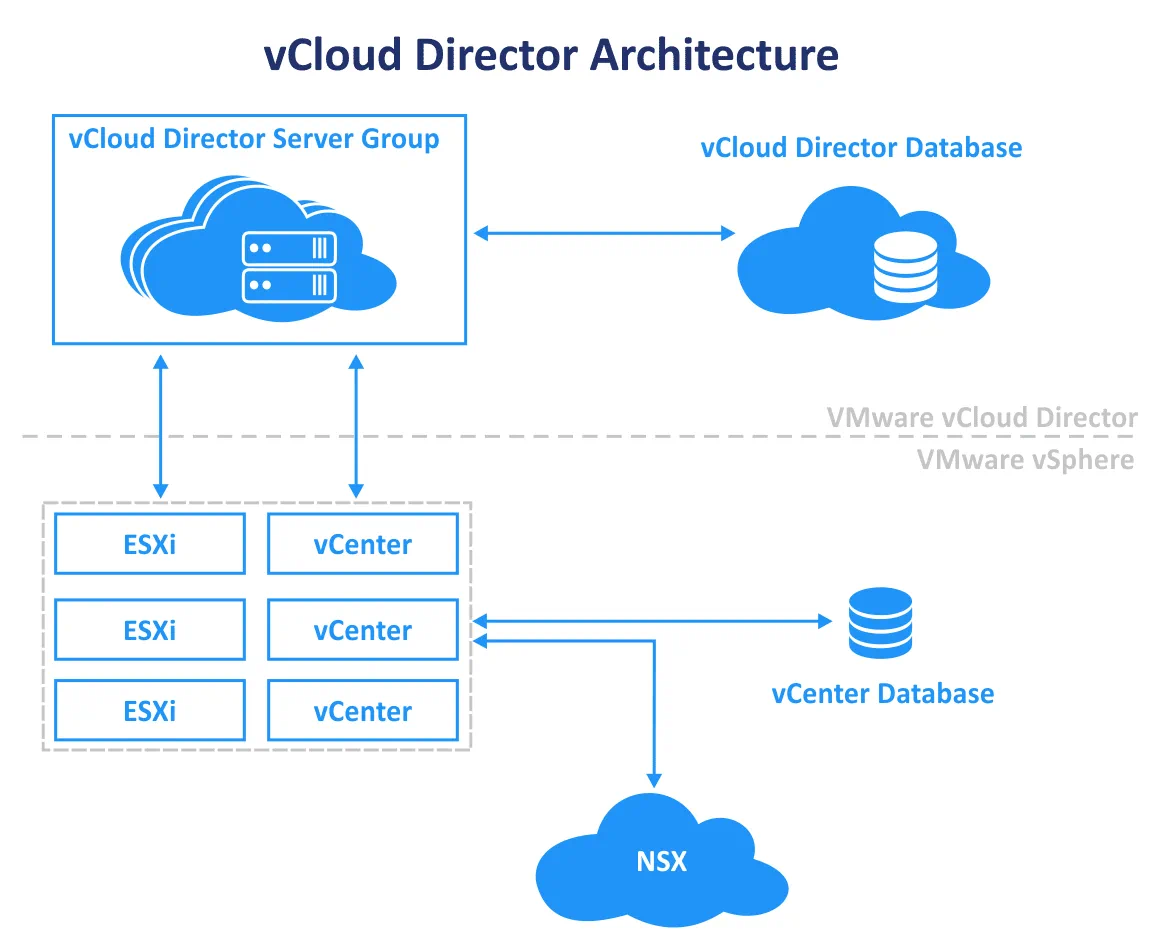
VMware vCloud Director is installed as an appliance that contains the embedded PostgreSQL database or installed on a Linux machine manually (in this case, an external database must be configured). After installation, you can integrate vCloud Director with other VMware components and deploy multiple vCloud Director servers or appliances to ensure high availability. The VMware Director appliance is distributed as an OVA template and contains a VMware Photon OS, service groups, and PostgreSQL.
VMware vCloud Director provides a control panel with a graphical user interface (GUI) to allow self-service for clients. The web interface is HTML5-based. The global administrator creates accounts for tenants with the appropriate permissions. Then tenants can create VMs, provision resources for the VMs, run VMs, etc. At first glance, Cloud Director seems too complex for new users who don’t have experience with such enterprise-level products. However, after some practice, users appreciate the power and convenience due to the rich functionality and variety of options.
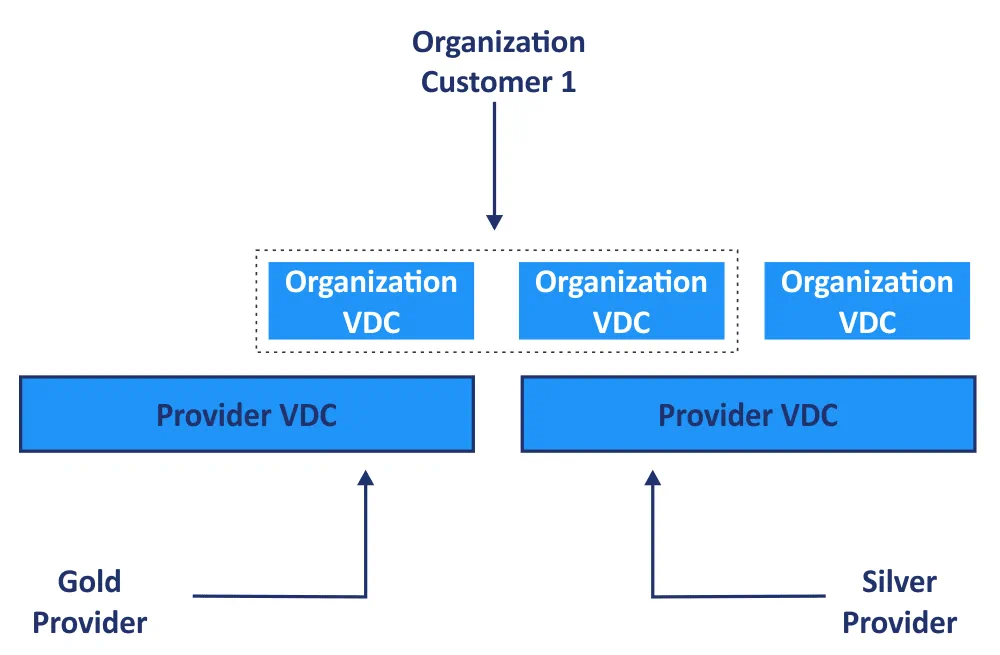
VMware vCloud Director is integrated with VMware vSphere and VMware vCenter to provide resource pools to create and run VMs. All the physical resources of a data center, such as computing resources, storage, and networking, are grouped into resource pools to be used by tenants in vCloud Director. VMware vSphere provides all the resources to vClo
ud Director to create a main shared pool, which is called a Provider vDC (virtual data center). The abstracted Provider vDC is used to allocate resources as separate units that are called Org vDC (organization virtual data center) to tenants. Org vDCs are connected to one or multiple networks and can utilize resources of different Provider vDCs to provide services of different classes (based on storage speed, availability, costs, etc.)
VMware vCloud Director vs VMware vSphere – What is the difference?
VMware vSphere includes ESXi hosts running directly on physical hardware and vCenter servers, which are used to manage ESXi hosts. VMware vSphere is used to allocate resources such as CPU, storage, memory, and network. Thus, vSphere components work at a lower level. You should add hosts, create clusters, distributed virtual switches, and other components of the virtual infrastructure in VMware vSphere.
VMware vCloud Director operates on a higher level and is used to abstract underlying physical resources, ESXi hosts, VMs, vCenter, etc. vCloud Director end users are not aware of the underlying physical infrastructure, ESXi hosts, and vCenter servers. VMware vCloud Director is used to create a cloud that can be used by end customers. VMware vCloud Director interacts with underlying vSphere components and infrastructure, as well as synchronizes with vSphere periodically. On the vCloud Director level, resource provisioning is automated. A user enters input parameters, then virtual machines, networks, and other resources are deployed in an optimal secure location automatically and seamlessly for a tenant. Rapid, transparent, and automated provisioning is done.
While a vCenter admin can see virtual data centers, which are logical units for management, a vCloud Director user (tenant) can see only organizational data centers, catalogs, users, and options to manage a virtual organizational data center. VMware vCloud Director administrators can see multiple organizations and underlying resources but cannot perform all administration operations for these resources as they do in vSphere.
Components and Concept
Let’s explore the main terms and concepts of VMware vCloud Director.
A virtual datacenter (vDC) is the environment where you can create virtual machines, vApps, VM folders with templates, etc.
A virtual machine is the basic unit of the virtual data center. You can create VMs from templates, create new VMs, and install a guest operating system from an ISO image.
Virtual Applications (vApps) is a container to store multiple VMs that operate together to run a multicomponent application (whose components are running on multiple VMs). VMware vApps are used to group and manage multiple VMs that perform common tasks. You can create vApp templates for fast deployment of vApps and VMs.
Libraries and catalogs are used to store virtual machines, templates, ISO installation images, etc. Users can upload their ISO files to catalogs.
The Org vDC network is the network of a virtual data center that is available for all vApps and VMs. The Org vDC network can be either isolated without internet access and routed with internet access.
The vApp network is a network that works only inside one vApp for vApp components (VMs). VMs of other vApps cannot access the network of this vApp. This approach provides an additional level of isolation between vApps. The vApp network has its own gateway for connecting to the Org vDC network.
An external network is a network connected to a VM directly without using the cloud edge gateway.
When a user creates a VM clone or creates a VM from a template, VMware allows the use of the Guest Personalization mechanism to change the GUID, VM name, host name, user password, virtual hardware options, etc., to make the new VM unique.
A managed service provider can assign tenant administrator permissions to a client to allow the client to create users, allocate resources within an organization, configure services, etc. A tenant administrator can configure public catalogs with VMs and VM templates and provide access to users. One of the main concepts of using the cloud configured with the vCloud Director is isolation. Tenants’ environments and their organizations’ virtual data centers are completely isolated from one another. In addition to high security, VMware Director is optimized for resource consumption.
Each tenant has a specific link for the associated organization to log into the web interface of the VMware Director by using own user account. VMware vCenter Chargeback Manager can be used by MSPs to calculate costs and provide billing.
How resources are allocated
When resources are needed for a tenant, they are allocated from an abstracted Provider vDC layer (for example, a user is starting a VM running a heavy application). When resources are not needed, they are turned back to the pool (for example, a VM is shut down).
There are three types of resource allocation for Organization vDC used by VMware vCloud Director – allocation pool, reservation pool, and pay as you go.
Allocation pool. The pre-defined percentage of resources is guaranteed, and the maximum available limit is set. The percentage of CPU and memory resources is defined.
Reservation pool. All resources are allocated. Guaranteed resources and maximum limits are equal. A user can edit limits and allocate resources for VMs at any time (limits are not set on the VM level by default).
Pay as you go. There are no guaranteed resources and defined limits set for reservation in the resource pool (resources seem unlimited for the resource pool). Resources are limited on the VM level. Use this option if you don’t know how many resources should be consumed.
The maximum number of VMs is set for each resource allocation model to limit the VM number in a vDC. From the point of view of an MSP, the provider can use elastic pool resources rationally and buy new hardware when there are no free resources.
Additional components
The functionality of the vCloud Director can be extended by using APIs, SDKs, and plug-ins. VMware vCloud Director provides APIs and SDKs to create custom applications and automate workflows. APIs were changed with the release of different VMware Director versions. VMware recommends that you use the latest API version.
VMware vCloud Director plug-ins are available to extend the functionality of VMware Director, service provider admin portal, and tenant portal. Developers can create their own plug-ins by using the tools mentioned above.
VMware vShield (VMware vCloud Networking and Security) is supported to improve security for network services.
Kubernetes and containers are supported in the latest versions of VMware vCloud Director with VMware Container Service Extension (CSE). An MSP provides Kubernetes as a service with these features to tenants. In VMware vCloud Director v.10.2, the Container Service Extension plug-in is enabled by default, and you don’t need to install this plug-in manually (just publish the plug-in for tenants).
VMware Director and NSX
VMware vCloud Director is integrated with VMware NSX, which allows you to configure a complex virtualized network in a software-defined data center (NSX-V and NSX-T are supported). As a result, users can create a customized network topology in a virtual data center to connect VMs to the network without the need to know about underlying physical network equipment. The NSX network consists of logical switches, routers, firewalls, load balancers, VPN, and additional security features. NSX-T Migration Tool allows you to migrate from VMware NSX-V to NSX-T.
Integration of vCloud Director with NSX provides the following features.
Distributed firewall. Manage security policies granularly, including rules for Org vDC traffic. Tenants can configure rules for north-south and east-west traffic management.
Dynamic routing. Use Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) and Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) to create routing tables automatically and dynamically to perform routing between VMware NSX edge gateways. Dynamic routing removes the need to configure routes manually, and this saves time when VMs from different Org vDCs must communicate with each other.
Tenant layer 2 VPN (Virtual Private Network) is used to create hybrid clouds. This feature allows tenants to create a tunnel between an Org vDC network and physical network of an organization (on-site).
Tenant SSL2 VPN is an additional option for remote access.
Load balancing allows service providers to distribute inbound traffic to meet the SLA (Service Level Agreement).
Advantages of vCloud Director
Let’s summarize the advantages of VMware vCloud Director:
- Fast and automated provisioning of VMs and their resources
- Multi-tenancy is the main concept for MSPs that reduces administration efforts
- Integration with other VMware products
- A wide range of settings, operational efficiency
- Flexible resource management
- High security and logical isolation of virtual datacenters, vApps, and VMs
Conclusion
VMware vCloud Director is a useful solution for managed service providers who provide infrastructure as a service (IaaS) by using the VMware vSphere virtualization platform to run virtual machines and containers. Support of multi-tenancy is ideal for MSPs due to optimization of administration efforts, cost-effectiveness for providers, logical isolation, and high security for tenant (client) resources in the cloud. Integration with VMware NSX allows users to configure virtual networks for their VMs. The wide range of settings makes VMware vCloud Director a great solution for MSPs and their clients.
If an MSP provides IaaS for customers to allow them to run virtual machines, it is a good idea to provide infrastructure as a service in combination with backup as a service (BaaS), replication as a service (RaaS), and disaster recovery as a service (DRaaS) to allow customers to protect and recover their data.
NAKIVO Backup & Replication is a universal data protection solution that supports installation in the multi-tenant mode and can be used by MSPs to provide BaaS, RaaS, and DRaaS for VMware vSphere and VMware Cloud Director environments. Download the Free Trial version that supports multi-tenancy for MSPs and try VMware vSphere backup and VMware Cloud Director backup along with the full feature set in your own environment.